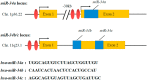
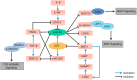
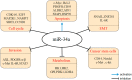
p53/MicroRNA-34 axis in cancer and beyond
- PMID: 37095919
- PMCID: PMC10121403
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15155
p53/MicroRNA-34 axis in cancer and beyond
Abstract
Cancer is serious endangers human life. After a long period of research and accumulation, people's understanding of cancer and the corresponding treatment methods are constantly developing. p53 is an important tumor suppressor gene. With the more in-depth understanding of the structure and function of p53, the more importance of this tumor suppressor gene is realized in the process of inhibiting tumor formation. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are important regulatory molecules with a length of about 22nucleotides (nt), which belong to non-coding RNA and play an important role in the occurrence and development of tumors. miR-34 is currently considered to be a master regulator of tumor suppression. The positive feedback regulatory network formed by p53 and miR-34 can inhibit the growth and metastasis of tumor cells and inhibit tumor stem cells. This review focuses on the latest progress of p53/miR-34 regulatory network, and discusses its application in tumor diagnosis and treatment.
Keywords: Signaling pathway; Tumor; miR-34; p53.
©2023PublishedbyElsevierLtd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[miR-34s--a tumor suppression protein p53 highly related microRNA].Yi Chuan. 2010 May;32(5):423-30. doi: 10.3724/sp.j.1005.2010.00423. Yi Chuan. 2010. PMID: 20466628 Review. Chinese.
-
LINC00472 Acts as a Tumor Suppressor in NSCLC through KLLN-Mediated p53-Signaling Pathway via MicroRNA-149-3p and MicroRNA-4270.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019 Sep 6;17:563-577. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2019.06.003. Epub 2019 Jun 15. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019. Retraction in: Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2022 May 10;28:597. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2022.05.016. PMID: 31382188 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
MiR-223-3p functions as a tumor suppressor in lung squamous cell carcinoma by miR-223-3p-mutant p53 regulatory feedback loop.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Feb 12;38(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1079-1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30755230 Free PMC article.
-
The PTTG1-targeting miRNAs miR-329, miR-300, miR-381, and miR-655 inhibit pituitary tumor cell tumorigenesis and are involved in a p53/PTTG1 regulation feedback loop.Oncotarget. 2015 Oct 6;6(30):29413-27. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5003. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26320179 Free PMC article.
-
The p53/miR-34 axis in development and disease.J Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Jun;6(3):214-30. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mju003. Epub 2014 May 9. J Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24815299 Review.
Cited by
-
Non-coding RNAs: emerging biomarkers and therapeutic targets in cancer and inflammatory diseases.Front Oncol. 2025 Mar 10;15:1534862. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1534862. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40129920 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs as Regulators of Radiation-Induced Oxidative Stress.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Jul 6;46(7):7097-7113. doi: 10.3390/cimb46070423. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39057064 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of miRNA in adult ocular tumorigenesis.Front Mol Biosci. 2025 May 8;12:1459761. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1459761. eCollection 2025. Front Mol Biosci. 2025. PMID: 40406621 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predicting therapeutic responses in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma from TP53 mutation detected by cell-free DNA.Transl Cancer Res. 2023 Dec 31;12(12):3604-3617. doi: 10.21037/tcr-23-878. Epub 2023 Dec 11. Transl Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 38197078 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Long-Lasting Environmental Factors on Regulation Mediated by the miR-34 Family.Biomedicines. 2024 Feb 12;12(2):424. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12020424. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38398026 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sung H., Ferlay J., Siegel R.L., et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2021;71(3):209–249. - PubMed
-
- Chen W., Zheng R., Baade P.D., et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2016;66(2):115–132. - PubMed
-
- Mullard A. Addressing cancer's grand challenges. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020;19(12):825–826. - PubMed
-
- Wu Y.-L., Zhang L., Kim D.-W., et al. Phase ib/II study of capmatinib (INC280) plus gefitinib after failure of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitor therapy in patients with EGFR-mutated, MET factor-dysregulated non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018;36(31):3101–3109. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous