A facile room temperature method to recycle Cd from CdS
- PMID: 37095936
- PMCID: PMC10122037
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15229
A facile room temperature method to recycle Cd from CdS
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "A facile room temperature method to recycle Cd from CdS" [Heliyon 9(4) (April 2023) e15229].Heliyon. 2023 May 6;9(5):e15877. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15877. eCollection 2023 May. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37305464 Free PMC article.
Abstract
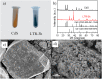
Cadmium-based semiconductors have a wide range of applications in light-emitting, energy conversion, photodetection and artificial photosynthesis. With the concern about the potential toxicity of Cd, it is necessary to recycle the element from the Cd based semiconductors. Commonly, the precipitation of Cd cations with S2- is deemed as the end point of recycling. However, actually, CdS is easy to be oxidized and released into the environment and accumulate in the food chain. It still remains challenges on how to refine the Cd element and convert it to the raw material. Herein, we demonstrate a facile room temperature method for recycling Cd from CdS. Cd can be produced from CdS within 3 h with the help of the lithium-ethylenediamine solution. DFT calculations further confirm that the high surface energy of (100) and (101) planes are selectively attacked by the solvated electrons in the solution, which is in good accordance with the XRD, STEM-HAADF and XPS characterizations. With a total recovery efficiency of 88%, Cd is successfully recovered from the CdS powder. This method provides a new perspective on the treatment of Cd-based semiconductor waste, which is of great significance for the recycling of cadmium metal.
Keywords: Cadmium; Cadmium recycling; Cadmium sulphide; Room temperature; Solution process.
©2023PublishedbyElsevierLtd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Luyang Wang, Ph.D. reports financial support was provided by National Natural Science Foundation of China. Ran Jia reports financial support was provided by Science and Technology Research Program of Education Department of Jilin Province. Yuanmin Zhu reports financial support was provided by Shenzhen Basic Research Program. Lei Ma reports financial support was provided by Foundation for Young Innovative Talents in Higher Education of Guangdong. Luyang Wang has patent #ZL201811399399X issued to Shenzhen Technology University.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Hydrated electrons mediated in-situ construction of cubic phase CdS/Cd thin layer on a millimeter-scale support for photocatalytic hydrogen evolution.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2022 Feb;607(Pt 1):769-781. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2021.09.039. Epub 2021 Sep 8. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2022. PMID: 34536934
-
Development of highly sensitive cadmium iondashselective electrodes by titration method and its application to cadmium ion determination in industrial waste water.Talanta. 1997 Apr;44(4):697-704. doi: 10.1016/s0039-9140(96)02109-1. Talanta. 1997. PMID: 18966791
-
Tweaking the Physics of Interfaces between Monolayers of Buckled Cadmium Sulfide for a Superhigh Piezoelectricity, Excitonic Solar Cell Efficiency, and Thermoelectricity.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020 Apr 15;12(15):18123-18137. doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c00864. Epub 2020 Apr 7. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020. PMID: 32223217
-
Cadmium pigments in consumer products and their health risks.Sci Total Environ. 2019 Mar 20;657:1409-1418. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.096. Epub 2018 Dec 10. Sci Total Environ. 2019. PMID: 30677907 Review.
-
Recovery methods and regulation status of waste lithium-ion batteries in China: A mini review.Waste Manag Res. 2019 Nov;37(11):1142-1152. doi: 10.1177/0734242X19857130. Epub 2019 Jun 27. Waste Manag Res. 2019. PMID: 31244410 Review.
References
-
- Al-Kuhaili M. Photoelectric properties of highly conductive samarium-doped cadmium telluride thin films for photovoltaic applications. Sol. Energy. 2021:213 163–171. doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2020.11.028. - DOI
-
- Cheng L., Xiang Q., Liao Y., Zhang H. CdS-based photocatalysts. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018;11(6):1362–1391. doi: 10.1039/C7EE03640J. - DOI
-
- Qu J., Meng X., Zhang Y., Meng Q., Tao Y., Hu Q., Jiang X., You H., Shoemaker C.A. A combined system of microwave-functionalized rice husk and poly-aluminium chloride for trace cadmium-contaminated source water purification: exploration of removal efficiency and mechanism. J. Hazard Mater. 2019;379 doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.120804. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

