Characterization of genotype IV hepatitis E virus-like particles expressed in E.coli
- PMID: 37095953
- PMCID: PMC10122030
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15284
Characterization of genotype IV hepatitis E virus-like particles expressed in E.coli
Abstract
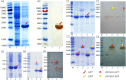
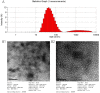
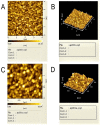
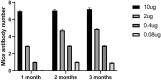
HEV (Hepatitis E virus) is an infectious disease transmitted between humans and animals, which poses a severe threat to the biological safety and property throughout the world. The disease is especially severe in patients with potential liver cirrhosis and women during pregnancy. There is no specific and thorough HEV treatment at present. The development of hepatitis E virus vaccine is vital to the prevention of viral hepatitis worldwide. Since HEV cannot grow adequately in vitro, vaccine developed by devitalized virus particles does not work. Exploration of HEV-like structures is essential for the development of functional vaccines against HEV infection. ORF2 encodes the structural proteins of HEV, some of which can automatically assemble into virus-like particles (VLP) in this experiment, the recombinant capsid protein p27 was expressed in E. coli and the VLP formed by p27 was used to immunize mice. The results showed that the VLP formed by recombinant P27 had similar particle size to that of HEV; the immune dose produced by p27 was positively correlated with the immune effect. Compared with other genetic engineering subunit vaccines, P27 protein has a better application prospect.
Keywords: HEV vaccine; Hepatitis E; The recombinant capsid protein p27; Virus-like particles.
©2023PublishedbyElsevierLtd.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest. The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Production of capsid proteins of rat hepatitis E virus in Escherichia coli and characterization of self-assembled virus-like particles.Virus Res. 2021 Sep;302:198483. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2021.198483. Epub 2021 Jun 17. Virus Res. 2021. PMID: 34146611
-
Induction of antibody response against hepatitis E virus (HEV) with recombinant human papillomavirus pseudoviruses expressing truncated HEV capsid proteins in mice.Vaccine. 2008 Dec 2;26(51):6602-7. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2008.09.035. Vaccine. 2008. PMID: 18835319
-
Generation in yeast and antigenic characterization of hepatitis E virus capsid protein virus-like particles.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018 Jan;102(1):185-198. doi: 10.1007/s00253-017-8622-9. Epub 2017 Nov 15. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29143081
-
Progress in the Production of Virus-Like Particles for Vaccination against Hepatitis E Virus.Viruses. 2020 Jul 30;12(8):826. doi: 10.3390/v12080826. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32751441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression and characterization of hepatitis E virus-like particles and non-virus-like particles from insect cells.Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2016 May;63(3):362-70. doi: 10.1002/bab.1379. Epub 2015 Jul 6. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2016. PMID: 25824972 Review.
Cited by
-
Vaccination Strategies and Research Gaps in Hepatitis E Virus for Special Populations.Vaccines (Basel). 2025 Jun 9;13(6):621. doi: 10.3390/vaccines13060621. Vaccines (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40573952 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Khaskheli M., Baloch S., Sheeba A., Baloch S. Hepatitis E-A preventable health issue-endangering pregnant women's life and foetal outcomes. JPMA (J. Pak. Med. Assoc.) 2015;65:655–659. - PubMed
-
- Organization W.H. World Health Organization; 2012. Prevention and Control of Viral Hepatitis Infection: Framework for Global Action.
-
- Xiaoli H. E. Doctor Of Liver; 2019. The Neglected Hepatitis -- Hepatitis; p. 2.
-
- Navaneethan U. Seroprevalence of hepatitis E infection in pregnancy-More questions than answers. Indian J. Med. Res. 2009;130:677–679. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

