A cell-permeable peptide inhibitor of p55PIK signaling alleviates suture-induced corneal neovascularization and inflammation
- PMID: 37095989
- PMCID: PMC10121607
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14869
A cell-permeable peptide inhibitor of p55PIK signaling alleviates suture-induced corneal neovascularization and inflammation
Abstract
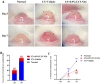
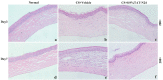
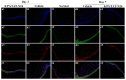
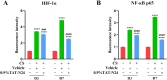
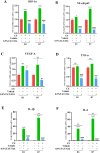
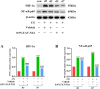
To prepare an ophthalmic solution with a cell-permeable TAT peptide (TAT-N24) as the main cell-permeable peptide inhibitor of p55PIK signaling and observe its therapeutic effect on suture-induced corneal neovascularization (CNV) in rats. Sprague-Dawley rats were used to establish a corneal suture (CS) model of CNV. The vehicle and 0.9% TAT-N24 ophthalmic solution was topically administered. CNV induction was assessed on the basis of the clinical performance of each group. Hematoxylin-eosin staining was used to observe pathological changes, and immunohistochemical staining and confocal immunofluorescence were used to determine the localization of factors associated with corneal tissue. The mRNA expression levels of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1α), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF-A), nuclear transcription factor κB (NF-κB p65), tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), and interleukin (IL)-6 were determined using real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Western blotting was performed to detect the protein expression levels of HIF-1α and NF-κB p65. TAT-N24 slowed CNV production and reduced the expression of HIF-1α and inflammatory factors in CS models. The mRNA levels of HIF-1α, VEGF-A, NF-kB, TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 significantly decreased. Moreover, the protein levels of HIF-1α and NF-κB p65 were significantly decreased. TAT-N24 can treat CNV and ocular inflammation by inhibiting the HIF-1α/NF-κB signaling pathway in CS. In the early treatment of corneal foreign body trauma, topical application of TAT-N24 can not only reduce the inflammatory response but also inhibit corneal neovascularization.
Keywords: Corneal neovascularization; Corneal suture; HIF-1α; Inflammation; NF-κB; P55PIK; TAT-N24.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A cell-permeable peptide inhibitor of p55PIK signaling alleviates ocular inflammation in mouse models of uveitis.Exp Eye Res. 2020 Oct;199:108180. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2020.108180. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Exp Eye Res. 2020. PMID: 32777209
-
Effects of the 24 N-terminal amino acids of p55PIK on endotoxinstimulated release of inflammatory cytokines by HaCaT cells.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2013 Aug;33(4):587-593. doi: 10.1007/s11596-013-1163-2. Epub 2013 Aug 1. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2013. PMID: 23904382
-
Celastrol nanomicelles attenuate cytokine secretion in macrophages and inhibit macrophage-induced corneal neovascularization in rats.Int J Nanomedicine. 2016 Nov 18;11:6135-6148. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S117425. eCollection 2016. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016. PMID: 27920521 Free PMC article.
-
κ-opioid receptor agonists may alleviate intestinal damage in cardiopulmonary bypass rats by inhibiting the NF-κB/HIF-1α pathway.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Jul;20(1):325-334. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.8685. Epub 2020 Apr 23. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32509012 Free PMC article.
-
Lactate modulates microglial inflammatory responses after oxygen-glucose deprivation through HIF-1α-mediated inhibition of NF-κB.Brain Res Bull. 2023 Apr;195:1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2023.02.002. Epub 2023 Feb 4. Brain Res Bull. 2023. PMID: 36746287
Cited by
-
Topical Ocular Drug Delivery: The Impact of Permeation Enhancers.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Mar 31;17(4):447. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17040447. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40284442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A SU6668 pure nanoparticle-based eyedrops: toward its high drug Accumulation and Long-time treatment for corneal neovascularization.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 May 27;22(1):290. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02510-8. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 38802884 Free PMC article.
-
Toxicity Studies of Cardiac-Targeting Peptide Reveal a Robust Safety Profile.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jan 4;16(1):73. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16010073. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38258084 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

