System Performance and User Feedback Regarding Wearable Bioimpedance System for Multi-Site Knee Tissue Monitoring: Free-Living Pilot Study With Healthy Adults
- PMID: 37096020
- PMCID: PMC10122869
- DOI: 10.3389/felec.2022.824981
System Performance and User Feedback Regarding Wearable Bioimpedance System for Multi-Site Knee Tissue Monitoring: Free-Living Pilot Study With Healthy Adults
Abstract
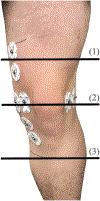
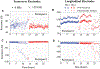
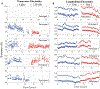
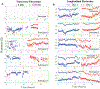
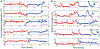
Knee-focused wearable devices have the potential to support personalized rehabilitation therapies by monitoring localized tissue alterations related to activities that reduce functional symptoms and pain. However, supporting these applications requires reported data to be reliable and accurate which can be challenging in the unsupervised free-living conditions that wearable devices are deployed. This pilot study has assessed a knee-focused wearable sensor system to quantify 1) system performance (operation, rates of data artifacts, environment impacts) to estimate realistic targets for reliable data with this system and 2) user experiences (comfort, fit, usability) to help inform future designs to increase usability and adoption of knee-focused wearables. Study data was collected from five healthy adult participants over 2 days, with 84.5 and 35.9% of artifact free data for longitudinal and transverse electrode configurations. Small to moderate positive correlations were also identified between changes in resistance, temperature, and humidity with respect to acceleration to highlight how this system can be used to explore relationships between knee tissues and environmental/activity context.
Keywords: bioimpedance; knee; multi-modal; multi-site; wearable.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

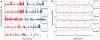
Similar articles
-
Threshold and Trend Artifacts in Localized Multi-Frequency Bioimpedance Measurements.IFAC Pap OnLine. 2021;54(15):55-60. doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2021.10.231. Epub 2021 Nov 2. IFAC Pap OnLine. 2021. PMID: 37097809 Free PMC article.
-
Flexible PCB Failures From Dynamic Activity and Their Impacts on Bioimpedance Measurements: A Wearable Case Study.IEEE Open J Circuits Syst. 2021;2:732-742. doi: 10.1109/OJCAS.2021.3122369. Epub 2021 Nov 24. IEEE Open J Circuits Syst. 2021. PMID: 34901875 Free PMC article.
-
A Nonproprietary Movement Analysis System (MoJoXlab) Based on Wearable Inertial Measurement Units Applicable to Healthy Participants and Those With Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Across a Range of Complex Tasks: Validation Study.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2020 Jun 16;8(6):e17872. doi: 10.2196/17872. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2020. PMID: 32543446 Free PMC article.
-
Augmenting Critical Care Patient Monitoring Using Wearable Technology: Review of Usability and Human Factors.JMIR Hum Factors. 2021 May 25;8(2):e16491. doi: 10.2196/16491. JMIR Hum Factors. 2021. PMID: 34032574 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wearable knee health system employing novel physiological biomarkers.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2018 Mar 1;124(3):537-547. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00366.2017. Epub 2017 Jul 27. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2018. PMID: 28751371 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Phase angle: a novel application of bioelectrical impedance technology in osteoarthritis screening and diagnosis.Clin Rheumatol. 2025 May;44(5):1877-1886. doi: 10.1007/s10067-025-07349-4. Epub 2025 Mar 25. Clin Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 40131594 Review.
-
A novel method for in-situ extracting bio-impedance model parameters optimized for embedded hardware.Sci Rep. 2023 Mar 28;13(1):5070. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-31860-w. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36977800 Free PMC article.
-
Localized Multi-Site Knee Bioimpedance as a Predictor for Knee Osteoarthritis Associated Pain Within Older Adults During Free-Living.IEEE Open J Eng Med Biol. 2023 Mar 13;4:1-10. doi: 10.1109/OJEMB.2023.3256181. eCollection 2023. IEEE Open J Eng Med Biol. 2023. PMID: 37138591 Free PMC article.
-
Segmental Tissue Resistance of Healthy Young Adults during Four Hours of 6-Degree Head-Down-Tilt Positioning.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Mar 3;23(5):2793. doi: 10.3390/s23052793. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36904995 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Critcher S, and Freeborn TJ (2020). “Multi-site Impedance Measurement System Based on max30001 Integrated-Circuit,” in 2020 IEEE 63rd International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS) (IEEE), 381–386. doi:10.1109/mwscas48704.2020.9184451 - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
