Hippocampal conjunctive and complementary CA1 populations relate sensory events to movement
- PMID: 37096033
- PMCID: PMC10121467
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106481
Hippocampal conjunctive and complementary CA1 populations relate sensory events to movement
Abstract
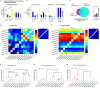
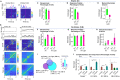
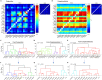
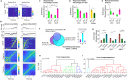
Hippocampal CA1 neurons respond to sensory stimuli during enforced immobility, movement, and their transitions in a new conveyor belt task. Head-fixed mice were exposed to light flashes or air streams while at rest, spontaneously moving, or running a fixed distance. Two-photon calcium imaging of CA1 neurons revealed that 62% of 3341 imaged cells were active during one or more of 20 sensorimotor events. Of these active cells, 17% were active for any given sensorimotor event, with a higher proportion during locomotion. The study found two types of cells: Conjunctive cells that were active across multiple events, and complementary cells that were active only during individual events, encoding novel sensorimotor events or their delayed repetitions. The configuration of these cells across changing sensorimotor events may signify the role of hippocampus in functional networks integrating sensory information with ongoing movement making it suitable for movement guidance.
Keywords: Health sciences; Neuroscience.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

