Adipocyte-derived chemerin rescues lipid overload-induced cardiac dysfunction
- PMID: 37096038
- PMCID: PMC10121453
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106495
Adipocyte-derived chemerin rescues lipid overload-induced cardiac dysfunction
Abstract
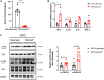
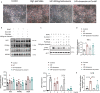
Chemerin, an adipocyte-secreted protein, has been recently suggested to be linked to metabolic syndrome and cardiac function in obese and diabetes mellitus. This study aimed to investigate the potential roles of adipokine chemerin on high fat-induced cardiac dysfunction. Chemerin (Rarres2) knockout mice, which were fed with either a normal diet or a high-fat diet for 20 weeks, were employed to observe whether adipokine chemerin affected lipid metabolism, inflammation, and cardiac function. Firstly, we found normal metabolic substrate inflexibility and cardiac function in Rarres2 -/- mice with a normal diet. Notably, in a high-fat diet, Rarres2 -/- mice showed lipotoxicity, insulin resistance, and inflammation, thus causing metabolic substrate inflexibility and cardiac dysfunction. Furthermore, by using in vitro model of lipid-overload cardiomyocytes, we found chemerin supplementation reversed the lipid-induced abnormalities above. Herein, in the presence of obesity, adipocyte-derived chemerin might function as an endogenous cardioprotective factor against obese-related cardiomyopathy.
Keywords: Cell biology; Cellular physiology; Physiology.
© 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Liu Y., Steinbusch L.K.M., Nabben M., Kapsokalyvas D., van Zandvoort M., Schönleitner P., Antoons G., Simons P.J., Coumans W.A., Geomini A., et al. Palmitate-induced vacuolar-type H(+)-ATPase inhibition feeds forward into insulin resistance and contractile dysfunction. Diabetes. 2017;66:1521–1534. doi: 10.2337/db16-0727. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

