Premature termination of transcription is shaped by Rho and translated uORFS in Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- PMID: 37096044
- PMCID: PMC10122055
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106465
Premature termination of transcription is shaped by Rho and translated uORFS in Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Abstract
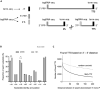
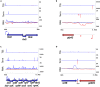
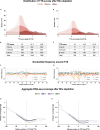
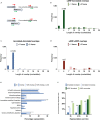
Little is known about the decisions behind transcription elongation versus termination in the human pathogen Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M.TB). By applying Term-seq to M.TB we found that the majority of transcription termination is premature and associated with translated regions, i.e., within previously annotated or newly identified open reading frames. Computational predictions and Term-seq analysis, upon depletion of termination factor Rho, suggests that Rho-dependent transcription termination dominates all transcription termination sites (TTS), including those associated with regulatory 5' leaders. Moreover, our results suggest that tightly coupled translation, in the form of overlapping stop and start codons, may suppress Rho-dependent termination. This study provides detailed insights into novel M.TB cis-regulatory elements, where Rho-dependent, conditional termination of transcription and translational coupling together play major roles in gene expression control. Our findings contribute to a deeper understanding of the fundamental regulatory mechanisms that enable M.TB adaptation to the host environment offering novel potential points of intervention.
Keywords: Biological sciences; Molecular biology; Molecular mechanism of gene regulation.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Schnappinger D., Ehrt S., Voskuil M.I., Liu Y., Mangan J.A., Monahan I.M., Dolganov G., Efron B., Butcher P.D., Nathan C., Schoolnik G.K. Transcriptional adaptation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis within macrophages: insights into the phagosomal environment. J. Exp. Med. 2003;198:693–704. doi: 10.1084/jem.20030846. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

