CircHECTD1 promoted MIRI-associated inflammation via inhibiting miR-138-5p and upregulating ROCK2
- PMID: 37096660
- PMCID: PMC11895932
- DOI: 10.1002/kjm2.12686
CircHECTD1 promoted MIRI-associated inflammation via inhibiting miR-138-5p and upregulating ROCK2
Abstract
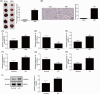
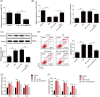
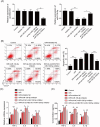
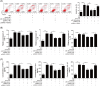
Myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury (MIRI) was often observed after surgeries, causing a lot of suffering to patients. Inflammation and apoptosis were critical determinants during MIRI. We conveyed experiments to reveal the regulatory functions of circHECTD1 in MIRI development. The Rat MIRI model was established and determined by 2,3,5-triphenyl tetrazolium chloride (TTC) staining. We analyzed cell apoptosis using TUNEL and flow cytometry. Proteins expression was evaluated by western blot. The RNA level was determined by qRT-PCR. Secreted inflammatory factors were analyzed by ELISA assay. To predict the interaction sequences on circHECTD1, miR-138-5p, and ROCK2, bioinformatics analysis was performed. Dual-luciferase assay was used to confirm these interaction sequences. CircHECTD1 and ROCK2 were upregulated in the rat MIRI model, while miR-138-5p was decreased. CircHECTD1 knockdown alleviated H/R-induced inflammation in H9c2 cells. Direct interaction and regulation of circHECTD1/miR-138-5p and miR-138-5p/ROCK2 were confirmed by dual-luciferase assay. CircHECTD1 promoted H/R-induced inflammation and cell apoptosis by inhibiting miR-138-5p. miR-138-5p alleviated H/R-induced inflammation, while ectopic ROCK2 antagonized such effect of miR-138-5p. Our research suggested that the circHECTD1-modulated miR-138-5p suppressing is responsible for ROCK2 activation during H/R-induced inflammatory response, providing a novel insight into MIRI-associated inflammation.
Keywords: ROCK2; circHECTD1; inflammation; ischemia/reperfusion injury; miR-138-5p.
© 2023 The Authors. The Kaohsiung Journal of Medical Sciences published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Kaohsiung Medical University.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
miR-92a-1-5p targets MEF2A to induce insulin resistance in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2025 Jul 1;768:151938. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2025.151938. Epub 2025 May 2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2025. PMID: 40345013
-
Long Non-coding RNA PVT1 Inhibits miR-30c-5p to Upregulate Rock2 to Modulate Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Through MAPK Signaling Pathway Activation.Mol Neurobiol. 2021 Nov;58(11):6032-6048. doi: 10.1007/s12035-021-02539-y. Epub 2021 Aug 26. Mol Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 34436749
-
Silencing of Long noncoding RNA SOX2-OT relieves myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through up-regulating microRNA-146a-5p.Bratisl Lek Listy. 2023;124(2):143-150. doi: 10.4149/BLL_2023_022. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2023. PMID: 36598302
-
Exosomes of bone-marrow stromal cells inhibit cardiomyocyte apoptosis under ischemic and hypoxic conditions via miR-486-5p targeting the PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.Thromb Res. 2019 May;177:23-32. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2019.02.002. Epub 2019 Feb 2. Thromb Res. 2019. PMID: 30844685
-
Circ_0114428 knockdown inhibits ROCK2 expression to assuage lipopolysaccharide-induced human pulmonary alveolar epithelial cell injury through miR-574-5p.J Physiol Sci. 2024 Jan 31;74(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s12576-023-00891-3. J Physiol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38297223 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Function of Circular RNAs in Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury: Underlying Mechanisms and Therapeutic Advancement.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2025 Aug;39(4):875-886. doi: 10.1007/s10557-024-07557-1. Epub 2024 Jan 30. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2025. PMID: 38289452 Review.
-
Shen-fu Injection Modulates HIF- 1α/BNIP3-Mediated Mitophagy to Alleviate Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2025 Jun;25(6):898-914. doi: 10.1007/s12012-025-09993-3. Epub 2025 Apr 17. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40246789
-
CircRNA Networks in CAD: Multi-Cellular Mechanisms and Clinical Potential.Int J Gen Med. 2025 Jun 12;18:3129-3150. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S524189. eCollection 2025. Int J Gen Med. 2025. PMID: 40529348 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Li J, Sun D, Li Y. Novel findings and therapeutic targets on cardioprotection of ischemia/ reperfusion injury in STEMI. Curr Pharm Des. 2019;25(35):3726–39. - PubMed
-
- Carney EF. Inflammation: activated protein C inhibits inflammasome activation in IRI. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2017;13(11):662. - PubMed
-
- Bai XF, Niu RZ, Liu J, Pan XD, Wang F, Yang W, et al. Roles of noncoding RNAs in the initiation and progression of myocardial ischemia‐reperfusion injury. Epigenomics. 2021;13(9):715–43. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

