Changes in Cardiac Structure and Function After Kidney Transplantation: A New Perspective Based on Strain Imaging
- PMID: 37096675
- PMCID: PMC10133806
- DOI: 10.4250/jcvi.2022.0125
Changes in Cardiac Structure and Function After Kidney Transplantation: A New Perspective Based on Strain Imaging
Abstract
Background: We aimed to investigate left ventricular (LV) global longitudinal strain (GLS) in end-stage renal disease patients and its change after kidney transplantation (KT).
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed patients who underwent KT between 2007 and 2018 at two tertiary centers. We analyzed 488 patients (median age, 53 years; 58% male) who had obtained echocardiography both before and within 3 years after KT. Conventional echocardiography and LV GLS assessed by two-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiography were comprehensively analyzed. Patients were classified into three groups according to the absolute value of pre-KT LV GLS (|LV GLS|). We compared longitudinal changes of cardiac structure and function according to pre-KT |LV GLS|.
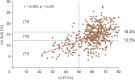
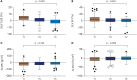
Results: Correlation between pre-KT LV EF and |LV GLS| were statistically significant, but the constant was not high (r = 0.292, p < 0.001). |LV GLS| was widely distributed at corresponding LV EF, especially when the LV EF was > 50%. Patients with severely impaired pre-KT |LV GLS| had significantly larger LV dimension, LV mass index, left atrial volume index, and E/e' and lower LV EF, compared to mildly and moderately reduced pre-KT |LV GLS|. After KT, the LV EF, LV mass index, and |LV GLS| were significantly improved in three groups. Patients with severely impaired pre-KT |LV GLS| showed the most prominent improvement of LV EF and |LV GLS| after KT, compared to other groups.
Conclusions: Improvements in LV structure and function after KT were observed in patients throughout the full spectrum of pre-KT |LV GLS|.
Keywords: Global longitudinal strain; Kidney transplantation; Left ventricle.
Copyright © 2023 Korean Society of Echocardiography.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Global longitudinal strain and global circumferential strain by speckle-tracking echocardiography and feature-tracking cardiac magnetic resonance imaging: comparison with left ventricular ejection fraction.J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2015 May;28(5):587-96. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2014.11.018. Epub 2015 Jan 7. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2015. PMID: 25577185
-
Time-dependent cardiac structural and functional changes after kidney transplantation: a multi-parametric cardiac magnetic resonance study.Eur Radiol. 2022 Aug;32(8):5265-5275. doi: 10.1007/s00330-022-08621-w. Epub 2022 Mar 11. Eur Radiol. 2022. PMID: 35275257
-
Feature-tracking cardiac magnetic resonance left ventricular global longitudinal strain improves 6 months after kidney transplantation associated with reverse remodeling, not myocardial tissue characteristics.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2021 Oct;37(10):3027-3037. doi: 10.1007/s10554-021-02284-2. Epub 2021 May 17. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2021. PMID: 33997925 Free PMC article.
-
Differences of myocardial systolic deformation and correlates of diastolic function in competitive rowers and young hypertensives: a speckle-tracking echocardiography study.J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2010 Nov;23(11):1190-8. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2010.07.010. Epub 2010 Sep 1. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2010. PMID: 20810245
-
Red cell distribution width and its relationship with global longitudinal strain in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: a study using two-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography.Kardiol Pol. 2018;76(3):580-585. doi: 10.5603/KP.a2017.0256. Epub 2018 Jan 3. Kardiol Pol. 2018. PMID: 29297194
Cited by
-
Evaluation of the effect of kidney transplantation on left ventricular myocardial work by noninvasive pressure-strain loops.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Jul 25;11:1370307. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1370307. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39119188 Free PMC article.
-
Left Ventricular Hypertrophy After Renal Transplantation: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Transplant Direct. 2024 May 17;10(6):e1647. doi: 10.1097/TXD.0000000000001647. eCollection 2024 Jun. Transplant Direct. 2024. PMID: 38769973 Free PMC article.
-
Strain Measurement for Assessment of Treatment Response: One Step Closer to Routine Clinical Practice.J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2023 Apr;31(2):105-107. doi: 10.4250/jcvi.2023.0001. J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2023. PMID: 37096676 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Left heart function and strain for predicting change in hemoglobin levels in pediatric kidney transplantation recipients.Front Pediatr. 2025 Mar 21;13:1452928. doi: 10.3389/fped.2025.1452928. eCollection 2025. Front Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40191645 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Novel Independent Correlations between Cellular Components of the Immune System and Strain-Related Indices of Myocardial Dysfunction in CKD Patients and Kidney Transplant Recipients without Established Cardiovascular Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 23;25(17):9162. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179162. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273110 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tonelli M, Wiebe N, Culleton B, et al. Chronic kidney disease and mortality risk: a systematic review. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17:2034–2047. - PubMed
-
- Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE, Hsu CY. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:1296–1305. - PubMed
-
- Löfman I, Szummer K, Dahlström U, Jernberg T, Lund LH. Associations with and prognostic impact of chronic kidney disease in heart failure with preserved, mid-range, and reduced ejection fraction. Eur J Heart Fail. 2017;19:1606–1614. - PubMed
-
- Marx N, Floege J. Cardiovascular disease in patients with chronic kidney disease. Herz. 2021;46:205. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

