In silico and in vivo demonstration of the regulatory mechanism of Qi-Ge decoction in treating NAFLD
- PMID: 37096878
- PMCID: PMC10281479
- DOI: 10.1080/07853890.2023.2200258
In silico and in vivo demonstration of the regulatory mechanism of Qi-Ge decoction in treating NAFLD
Abstract
Background: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), a chronic and progressive liver disease, often causes steatosis and steatohepatitis. Qi-Ge decoction (QGD) shows a good effect against NAFLD in the clinic. But the molecular mechanism for QGD in improving NAFLD is unknown.
Purpose: This study explored the molecular mechanism of QGD in NAFLD model rats using comprehensive network pharmacology, molecular docking and in vivo verification strategies.
Methods: Active components and targets of QGD were obtained from public database. The overlapped genes between QGD and NAFLD targets were analyzed by enrichment analysis. Active components and targets were used to predict molecular docking analysis. Finally, seven key targets were screened out and the gene expression were verified in the NAFLD rat's liver tissues after QGD treatment.
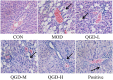
Results: Fifty-eight common QGD therapeutic targets were associated with NAFLD. Molecular docking demonstrated that seven targets had strong binding ability for the corresponding active ingredients. GO analysis identified 18 biological process entries, which were mainly related to regulation of lipid storage, lipid localization and peptide transport. KEGG analysis identified multiple signaling pathways, which were mainly associated with tumor necrosis factor signaling and NAFLD. In vivo data confirmed that the effect of QGD in the treatment of NAFLD was mainly exerted through improving liver steatosis and inflammatory cell infiltration. Additionally, QGD upregulated the expression of MAPK8 and ESR1 and downregulated the transcriptional expression of IL6, VEGFA, CASP3, EGFR and MYC. These targets may affect lipid metabolism by regulating lipid storage and inflammation.
Conclusion: The integration of results obtained in silico and in vivo indicated that QGD regulates multiple targets, biological processes and signaling pathways in NAFLD, which may represent a complex molecular mechanism by which QGD improves NAFLD.Key messagesQGD intervention is related to multiple biological processes such as inflammation, oxidation and cell apoptosis in NAFLD.Lipid and atherosclerosis, TNF signaling pathway, IL-17 signaling pathway, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications are the main pathways for QGD intervention NAFLD.The active components of QGD can form good binding with relevant target proteins through intermolecular forces, exhibiting excellent docking activity.
Keywords: NAFLD; Qi-ge decoction; in silico study; in vivo validation; molecular docking; network pharmacology.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures






Similar articles
-
Investigation of the potential mechanism of the Shugan Xiaozhi decoction for the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease based on network pharmacology, molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation.PeerJ. 2022 Nov 10;10:e14171. doi: 10.7717/peerj.14171. eCollection 2022. PeerJ. 2022. PMID: 36389420 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction and verification of the active ingredients and potential targets of Erhuang Quzhi Granules on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease based on network pharmacology.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Jul 15;311:116435. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116435. Epub 2023 Apr 5. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37023836
-
Therapeutic Effect and Mechanism Prediction of Fuzi-Gancao Herb Couple on Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024;27(5):773-785. doi: 10.2174/1386207326666230614102412. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024. PMID: 37317908
-
Natural products in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): Novel lead discovery for drug development.Pharmacol Res. 2023 Oct;196:106925. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2023.106925. Epub 2023 Sep 14. Pharmacol Res. 2023. PMID: 37714392 Review.
-
Ginseng and its functional components in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: therapeutic effects and multi-target pharmacological mechanisms.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 9;16:1540255. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1540255. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40271056 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In silico and in vivo verification of the mechanism of formononetin in treating hepatocellular carcinoma.Ann Med. 2024 Dec;56(1):2404550. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2404550. Epub 2024 Sep 20. Ann Med. 2024. PMID: 39301883 Free PMC article.
-
miR-128-3p inhibits intramuscular adipocytes differentiation in chickens by downregulating FDPS.BMC Genomics. 2023 Sep 12;24(1):540. doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09649-y. BMC Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37700222 Free PMC article.
-
Defective autophagy in vascular smooth muscle cells promote uremic accelerated atherosclerosis.Ren Fail. 2025 Dec;47(1):2538268. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2025.2538268. Epub 2025 Aug 13. Ren Fail. 2025. PMID: 40804030 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the Hub Genes Involved in Cadmium-Induced Hepatotoxicity.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025 Apr;203(4):2186-2205. doi: 10.1007/s12011-024-04307-0. Epub 2024 Jul 16. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025. PMID: 39012411
-
Qige San regulates paclitaxel resistance in esophageal cancer by targeting ferroptosis.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025 Aug 15;17(8):106783. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i8.106783. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40837755 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hung TC, Zhao N, Huang C, et al. . Exploring the mechanism of PingTang no.5 capsule on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease through network pharmacology and experimental validation. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;138:111408. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
