Advanced Methodology for Rapid Isolation of Single Myofibers from Flexor Digitorum Brevis Muscle
- PMID: 37097213
- PMCID: PMC10686193
- DOI: 10.1089/ten.TEC.2023.0012
Advanced Methodology for Rapid Isolation of Single Myofibers from Flexor Digitorum Brevis Muscle
Abstract
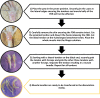
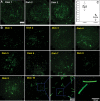
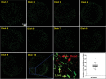
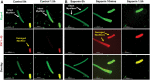
Isolated individual myofibers are valuable experimental models that can be used in various conditions to understand skeletal muscle physiology and pathophysiology at the tissue and cellular level. This report details a time- and cost-effective method for isolation of single myofibers from the flexor digitorum brevis (FDB) muscle in both young and aged mice. The FDB muscle was chosen for its documented history in single myofiber experiments. By modifying published methods for FDB myofiber isolation, we have optimized the protocol by first separating FDB muscle into individual bundles before the digestion, followed by optimizing the subsequent digestion medium conditions to ensure reproducibility. Morphological and functional assessments demonstrate a high yield of isolated FDB myofibers with sarcolemma integrity achieved in a shorter time frame than previous published procedures. This method could be also adapted to other types of skeletal muscle. Additionally, this highly reproducible method can greatly reduce the number of animals needed to yield adequate numbers of myofibers for experiments. Thus, this advanced method for myofiber isolation has the potential to accelerate research in skeletal muscle physiology and screening potential therapeutics "ex vivo" for muscle diseases and regeneration.
Keywords: FDB; flexor digitorum brevis; isolation; muscle physiology; myofiber.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Isolation, Culture, and Immunostaining of Skeletal Muscle Myofibers from Wildtype and Nestin-GFP Mice as a Means to Analyze Satellite Cell.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1556:51-102. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6771-1_4. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28247345
-
Isolation and culture of individual myofibers and their satellite cells from adult skeletal muscle.J Vis Exp. 2013 Mar 22;(73):e50074. doi: 10.3791/50074. J Vis Exp. 2013. PMID: 23542587 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and culture of skeletal muscle myofibers as a means to analyze satellite cells.Methods Mol Biol. 2013;946:431-68. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-128-8_28. Methods Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23179849 Free PMC article.
-
Regenerating Myofibers after an Acute Muscle Injury: What Do We Really Know about Them?Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 8;24(16):12545. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612545. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37628725 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Architecture and molecular machinery of skeletal myofibers: a systematic review of the structure-function relationships.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 May 20;13:1602607. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1602607. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40463839 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of high-intensity interval training and moderate-intensity continuous training on mitochondrial dynamics in human skeletal muscle.Front Physiol. 2025 Apr 17;16:1554222. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2025.1554222. eCollection 2025. Front Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40313872 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gollapudi SK, Michael JJ, Chandra M. Striated muscle dynamics. In: Reference Module in Biomedical Sciences. Elsevier, Amsterdam; 2014; 1–17. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128012383002518?v... [Last accessed: May 16, 2023].
-
- Stocum DL. Chapter 6—Regeneration of musculoskeletal tissues. In: Regenerative Biology and Medicine, 2nd ed. (Stocum DL. ed.) Academic Press: San Diego; 2012; pp. 127–160.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

