Three generations of mTOR kinase inhibitors in the activation of the apoptosis process in melanoma cells
- PMID: 37097377
- PMCID: PMC10409930
- DOI: 10.1007/s12079-023-00748-9
Three generations of mTOR kinase inhibitors in the activation of the apoptosis process in melanoma cells
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Three generations of mTOR kinase inhibitors in the activation of the apoptosis process in melanoma cells.J Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Sep;17(3):991. doi: 10.1007/s12079-023-00764-9. J Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37160591 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
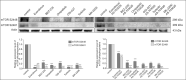
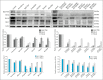
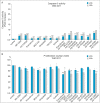
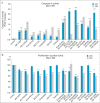
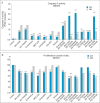
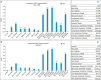
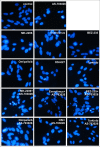
Many signaling pathways are involved in the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), and this serine/threonine kinase regulates the most important cellular processes such as cell proliferation, autophagy, and apoptosis. The subject of this research was the effect of protein kinase inhibitors involved in the AKT, MEK, and mTOR kinase signaling pathways on the expression of pro-survival proteins, activity of caspase-3, proliferation, and induction of apoptosis in melanoma cells. The following inhibitors were used: protein kinase inhibitors such as AKT-MK-2206, MEK-AS-703026, mTOR-everolimus and Torkinib, as well as dual PI3K and mTOR inhibitor-BEZ-235 and Omipalisib, and mTOR1/2-OSI-027 inhibitor in single-mode and their combinations with MEK1/2 kinase inhibitor AS-703026. The obtained results confirm the synergistic effect of nanomolar concentrations of mTOR inhibitors, especially the dual PI3K and mTOR inhibitors (Omipalisib, BEZ-235) in combination with the MAP kinase inhibitor (AS-703026) in the activation of caspase 3, induction of apoptosis, and inhibition of proliferation in melanoma cell lines. Our previous and current studies confirm the importance of the mTOR signal transduction pathway in the neoplastic transformation process. Melanoma is a case of a very heterogeneous neoplasm, which causes great difficulties in treating this neoplasm in an advanced stage, and the standard approach to this topic does not bring the expected results. There is a need for research on the search for new therapeutic strategies aimed at particular groups of patients. Effect of three generations of mTOR kinase inhibitors on caspase-3 activity, apoptosis and proliferation in melanoma cell lines.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Caspase-3 activity; Immunosuppressive treatment; Melanoma; Proliferation; mTOR inhibitors.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Primary cross-resistance to BRAFV600E-, MEK1/2- and PI3K/mTOR-specific inhibitors in BRAF-mutant melanoma cells counteracted by dual pathway blockade.Oncotarget. 2016 Jan 26;7(4):3947-65. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6600. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26678033 Free PMC article.
-
mTOR inhibitor Everolimus-induced apoptosis in melanoma cells.J Cell Commun Signal. 2019 Sep;13(3):357-368. doi: 10.1007/s12079-019-00510-0. Epub 2019 Mar 8. J Cell Commun Signal. 2019. PMID: 30848427 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological inhibition of mTORC1 but not mTORC2 protects against human disc cellular apoptosis, senescence, and extracellular matrix catabolism through Akt and autophagy induction.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019 Jun;27(6):965-976. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2019.01.009. Epub 2019 Feb 1. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019. PMID: 30716534
-
Rational combination of dual PI3K/mTOR blockade and Bcl-2/-xL inhibition in AML.Physiol Genomics. 2014 Jul 1;46(13):448-56. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00173.2013. Epub 2014 May 13. Physiol Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24824212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two hits are better than one: targeting both phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and mammalian target of rapamycin as a therapeutic strategy for acute leukemia treatment.Oncotarget. 2012 Apr;3(4):371-94. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.477. Oncotarget. 2012. PMID: 22564882 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Iron oxide nanoparticles induce ferroptosis via the autophagic pathway by synergistic bundling with paclitaxel.Mol Med Rep. 2023 Oct;28(4):198. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2023.13085. Epub 2023 Sep 8. Mol Med Rep. 2023. PMID: 37681444 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Basu D, Salgado CM, Bauer B, Khakoo Y, Patel JR, Hoehl RM, Bertolini DM, Zabec J, Brzozowski MR, Reyes-Múgica M. The Dual PI3K/mToR inhibitor omipalisib/GSK2126458 inhibits clonogenic growth in oncogenically-transformed cells from neurocutaneous melanocytosis. Cancer Genom Proteom. 2018;15(4):239–248. doi: 10.21873/cgp.20082. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ciolczyk-Wierzbicka D, Gil D, Laidler P (2012) The inhibition of cell proliferation using silencing of N-cadherin gene by siRNA process in human melanoma cell lines. Curr Med Chem 19(1):145–151. 10.2174/092986712803414006 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

