Transjugular intrahepatic collateral-systemic shunt is effective for cavernous transformation of the portal vein with variceal bleeding
- PMID: 37097537
- PMCID: PMC10386942
- DOI: 10.1007/s12072-023-10522-z
Transjugular intrahepatic collateral-systemic shunt is effective for cavernous transformation of the portal vein with variceal bleeding
Abstract
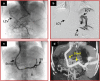
Background: The transjugular intrahepatic portal collateral-systemic shunt (transcollateral TIPS) is used to treat portal hypertension-related complications in patients with cavernous transformation of the portal vein (CTPV) and whose main portal vein cannot be recanalized. It is still not clear whether transcollateral TIPS can be as effective as portal vein recanalization-transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (PVR-TIPS). This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of transcollateral TIPS in the treatment of refractory variceal bleeding with CTPV.
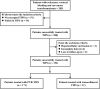
Methods: Patients with refractory variceal bleeding caused by CTPV were selected from the database of consecutive patients treated with TIPS in Xijing Hospital from January 2015 to March 2022. They were divided into the transcollateral TIPS group and the PVR-TIPS group. The rebleeding rate, overall survival, shunt dysfunction, overt hepatic encephalopathy (OHE) and operation-related complications were analyzed.
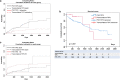
Results: A total of 192 patients were enrolled, including 21 patients with transcollateral TIPS and 171 patients with PVR-TIPS. Compared with the patients with PVR-TIPS, the patients with transcollateral TIPS had more noncirrhosis (52.4 vs. 19.9%, p = 0.002), underwent fewer splenectomies (14.3 vs. 40.9%, p = 0.018), and had more extensive thromboses (38.1 vs. 15.2%, p = 0.026). There were no differences in rebleeding, survival, shunt dysfunction, or operation-related complication rates between the transcollateral TIPS and PVR-TIPS groups. However, the OHE rate was significantly lower in the transcollateral TIPS group (9.5 vs. 35.1%, p = 0.018).
Conclusion: Transcollateral TIPS is an effective treatment for CTPV with refractory variceal bleeding.
Keywords: Cavernous transformation; Occlusive portal vein thrombosis; Refractory variceal bleeding; Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Jun Tie has no conflict of interest. Xiaoyuan Gou has no conflict of interest. Chuangye He has no conflict of interest. Kai Li has no conflict of interest. Xulong Yuan has no conflict of interest. Wenyuan Jia has no conflict of interest. Jing Niu has no conflict of interest. Na Han has no conflict of interest. Jiao Xu has no conflict of interest. Ying Zhu has no conflict of interest. Wenlan Wang has no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Senzolo M, Teresa MS, Rossetto V, Burra P, Cillo U, Boccagni P, et al. Prospective evaluation of anticoagulation and transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for the management of portal vein thrombosis in cirrhosis. Liver Int. 2012;32(6):919–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2012.02785.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Salem R, Vouche M, Baker T, Herrero JI, Caicedo JC, Fryer J, et al. Pretransplant portal vein recanalization-transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in patients with complete obliterative portal vein thrombosis. Transplantation. 2015;99(11):2347–2355. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000000729. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kallini JR, Gabr A, Kulik L, Ganger D, Lewandowski R, Thornburg B, et al. Noncirrhotic complete obliterative portal vein thrombosis: novel management using trans-splenic transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt with portal vein recanalization. Hepatology. 2016;63(4):1387–1390. doi: 10.1002/hep.28429. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

