Tibial fracture surgery in elderly mice caused postoperative neurocognitive disorder via SOX2OT lncRNA in the hippocampus
- PMID: 37098623
- PMCID: PMC10131420
- DOI: 10.1186/s13041-023-01024-y
Tibial fracture surgery in elderly mice caused postoperative neurocognitive disorder via SOX2OT lncRNA in the hippocampus
Abstract
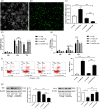
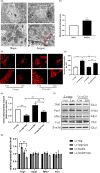
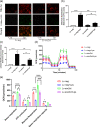
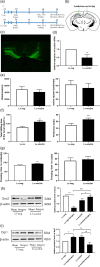
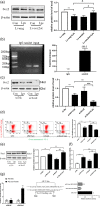
Increasing evidence indicates the major role of mitochondrial function in neurodegenerative disease. However, it is unclear whether mitochondrial dynamics directly affect postoperative neurocognitive disorder (PND). This study aimed to analyze the underlying mechanisms of mitochondrial dynamics in the pathogenesis of PND. Tibial fracture surgery was performed in elderly mice to generate a PND model in vivo. Cognitive behavior was evaluated 3 days post-surgery using novel object recognition and fear conditioning. A gradual increase in the SOX2OT mRNA level and decrease in the SOX2 mRNA level were noted, with impaired cognitive function, in the mice 3 days after tibial surgery compared with mice in the sham group. To evaluate the role of SOX2OT in PND, SOX2OT knockdown was performed in vitro and in vivo using lentivirus transfection in HT22 cells and via brain stereotactic injection of lentivirus, respectively. SOX2OT knockdown reduced apoptosis, inhibited oxidative stress, suppressed mitochondrial hyperdivision, attenuated surgery-induced cognitive dysfunction, and promoted downstream SOX2 expression in elderly mice. Furthermore, Sox2 alleviated mitochondrial functional damage by inhibiting the transcription of mitochondrial division protein Drp1. Our study findings indicate that SOX2OT knockout alleviates surgery-induced mitochondrial fission and cognitive function defects by upregulating the expression of Sox2 in mice, resulting in the inhibition of drp1 transcription. Therefore, regulation of the SOX2/Drp1 pathway may be a potential mechanism for the treatment of patients with PND.
Keywords: Drp1; Mitochondrial dynamics; Oxidative stress; Postoperative neurocognitive disorder; SOX2; SOX2OT.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Knockdown of long non-coding RNA SOX2OT downregulates SOX2 to improve hippocampal neurogenesis and cognitive function in a mouse model of sepsis-associated encephalopathy.J Neuroinflammation. 2020 Oct 25;17(1):320. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-01970-7. J Neuroinflammation. 2020. PMID: 33100215 Free PMC article.
-
The cold-inducible RNA-binding protein-Thioredoxin 1 pathway ameliorates mitochondrial dysfunction and mitochondrial dynamin-related protein 1 level in the hippocampus of aged mice with perioperative neurocognitive dysfunction.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Mar;30(3):e14433. doi: 10.1111/cns.14433. Epub 2023 Aug 29. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 37641878 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA SOX2OT Mediates Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Septic Cardiomyopathy.DNA Cell Biol. 2019 Nov;38(11):1197-1206. doi: 10.1089/dna.2019.4839. Epub 2019 Oct 16. DNA Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31618067
-
Long non-coding RNA SOX2OT: expression signature, splicing patterns, and emerging roles in pluripotency and tumorigenesis.Front Genet. 2015 Jun 17;6:196. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2015.00196. eCollection 2015. Front Genet. 2015. PMID: 26136768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The prognostic value of long noncoding RNA Sox2ot expression in various cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Chim Acta. 2018 Sep;484:52-59. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2018.05.038. Epub 2018 May 19. Clin Chim Acta. 2018. PMID: 29787741
Cited by
-
The role of lncRNAs related ceRNA regulatory network in multiple hippocampal pathological processes during the development of perioperative neurocognitive disorders.PeerJ. 2024 Aug 9;12:e17775. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17775. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39135955 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging role of long non-coding RNA SOX2-OT in cancers and non-malignant diseases.J Physiol Biochem. 2025 Feb;81(1):57-83. doi: 10.1007/s13105-024-01059-2. Epub 2024 Dec 20. J Physiol Biochem. 2025. PMID: 39702742 Review.
References
-
- Moller JT, Cluitmans P, Rasmussen LS, Houx P, Rasmussen H, Canet J, et al. Long-term postoperative cognitive dysfunction in the elderly ISPOCD1 study. ISPOCD investigators. International study of post-operative cognitive dysfunction. Lancet. 1998;351:857–861. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(97)07382-0. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

