Shared Decision Making for Choosing renAl Replacement Therapy in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients (SDM-ART trial): study protocol for randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 37098669
- PMCID: PMC10698061
- DOI: 10.23876/j.krcp.22.019
Shared Decision Making for Choosing renAl Replacement Therapy in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients (SDM-ART trial): study protocol for randomized clinical trial
Abstract
Background: Patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) should be educated about their condition so that they can initiate dialysis at the optimal time and make an informed choice between dialysis modalities. Shared decision-making (SDM) empowers patients to select their own treatment and improves patient outcomes. This study aimed to evaluate whether SDM affects the choice of renal replacement therapy among CKD patients.
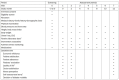
Methods: This is a multicenter, open-label, randomized, pragmatic clinical trial. A total of 1,194 participants with CKD who are considering renal replacement therapy were enrolled. The participants will be randomized into three groups in a 1:1:1 ratio: the conventional group, extensive informed decision-making group, and SDM group. Participants will be educated twice at months 0 and 2. Videos and leaflets will be provided to all patients. Patients in the conventional group will receive 5 minutes of education at each visit. The extensive informed decision-making group will receive more informed and detailed education using intensive learning materials for 10 minutes each visit. Patients in the SDM group will be educated for 10 minutes each visit according to illness perception and item-based analysis. The primary endpoint is the ratio of hemodialysis to peritoneal dialysis and kidney transplantation among the groups. Secondary outcomes include unplanned dialysis, economic efficiency, patient satisfaction, patient evaluation of the process, and patient adherence.
Discussion: The SDM-ART is an ongoing clinical study to investigate the effect of SDM on the choice of renal replacement therapy in patients with CKD.
Keywords: Chronic renal insufficiency; Peritoneal dialysis; Renal dialysis; Shared decision making.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Shared decision-making for renal replacement treatment and illness perception in patients with advanced chronic kidney disease.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2023 Aug 14;23(1):159. doi: 10.1186/s12911-023-02261-w. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2023. PMID: 37580719 Free PMC article.
-
Information about different treatment options and shared decision making in dialysis care - a retrospective survey among hemodialysis patients.BMC Health Serv Res. 2021 Jul 8;21(1):673. doi: 10.1186/s12913-021-06599-7. BMC Health Serv Res. 2021. PMID: 34238295 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of a shared decision-making program in reducing unplanned dialysis in advanced chronic kidney disease: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Nephrol. 2025 May 2;26(1):224. doi: 10.1186/s12882-025-04144-w. BMC Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40316919 Free PMC article.
-
Shared Decision-Making for a Dialysis Modality.Kidney Int Rep. 2021 Oct 30;7(1):15-27. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2021.10.019. eCollection 2022 Jan. Kidney Int Rep. 2021. PMID: 35005310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Shared Decision-Making and Patient Communication in Nephrology Practice.Adv Kidney Dis Health. 2024 Jan;31(1):5-12. doi: 10.1053/j.akdh.2023.12.003. Adv Kidney Dis Health. 2024. PMID: 38403394 Review.
Cited by
-
Status and trends in epidemiologic characteristics of diabetic end-stage renal disease: an analysis of the 2021 Korean Renal Data System.Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2024 Jan;43(1):20-32. doi: 10.23876/j.krcp.23.130. Epub 2024 Jan 25. Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2024. PMID: 38268124 Free PMC article.
-
Ongoing Peritoneal Dialysis Training at Home Allows for the Improvement of Patients' Empowerment: A Single Center Experience.J Clin Med. 2024 Jan 11;13(2):411. doi: 10.3390/jcm13020411. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38256544 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of Mobile Apps in Improving Medication Adherence Among Chronic Kidney Disease Patients: Systematic Review.J Med Internet Res. 2025 Apr 16;27:e53144. doi: 10.2196/53144. J Med Internet Res. 2025. PMID: 40239197 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kim SH, Jo MW, Go DS, Ryu DR, Park J. Economic burden of chronic kidney disease in Korea using national sample cohort. J Nephrol. 2017;30:787–793. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

