Yeasts Have Evolved Divergent Enzyme Strategies To Deconstruct and Metabolize Xylan
- PMID: 37098941
- PMCID: PMC10269524
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.00245-23
Yeasts Have Evolved Divergent Enzyme Strategies To Deconstruct and Metabolize Xylan
Abstract
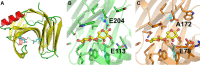
Together with bacteria and filamentous fungi, yeasts actively take part in the global carbon cycle. Over 100 yeast species have been shown to grow on the major plant polysaccharide xylan, which requires an arsenal of carbohydrate active enzymes. However, which enzymatic strategies yeasts use to deconstruct xylan and what specific biological roles they play in its conversion remain unclear. In fact, genome analyses reveal that many xylan-metabolizing yeasts lack expected xylanolytic enzymes. Guided by bioinformatics, we have here selected three xylan-metabolizing ascomycetous yeasts for in-depth characterization of growth behavior and xylanolytic enzymes. The savanna soil yeast Blastobotrys mokoenaii displays superior growth on xylan thanks to an efficient secreted glycoside hydrolase family 11 (GH11) xylanase; solving its crystal structure revealed a high similarity to xylanases from filamentous fungi. The termite gut-associated Scheffersomyces lignosus, in contrast grows more slowly, and its xylanase activity was found to be mainly cell surface-associated. The wood-isolated Wickerhamomyces canadensis, surprisingly, could not utilize xylan as the sole carbon source without the addition of xylooligosaccharides or exogenous xylanases or even co-culturing with B. mokoenaii, suggesting that W. canadensis relies on initial xylan hydrolysis by neighboring cells. Furthermore, our characterization of a novel W. canadensis GH5 subfamily 49 (GH5_49) xylanase represents the first demonstrated activity in this subfamily. Our collective results provide new information on the variable xylanolytic systems evolved by yeasts and their potential roles in natural carbohydrate conversion. IMPORTANCE Microbes that take part in the degradation of the polysaccharide xylan, the major hemicellulose component in plant biomass, are equipped with specialized enzyme machineries to hydrolyze the polymer into monosaccharides for further metabolism. However, despite being found in virtually every habitat, little is known of how yeasts break down and metabolize xylan and what biological role they may play in its turnover in nature. Here, we have explored the enzymatic xylan deconstruction strategies of three underexplored yeasts from diverse environments, Blastobotrys mokoenaii from soil, Scheffersomyces lignosus from insect guts, and Wickerhamomyces canadensis from trees, and we show that each species has a distinct behavior regarding xylan conversion. These findings may be of high relevance for future design and development of microbial cell factories and biorefineries utilizing renewable plant biomass.
Keywords: CAZymes; microbial co-cultures; xylan; xylanase; yeast.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genomic and secretomic analyses of Blastobotrys yeasts reveal key xylanases for biomass decomposition.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025 Aug 1;109(1):175. doi: 10.1007/s00253-025-13556-5. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40748385 Free PMC article.
-
CAZyme prediction in ascomycetous yeast genomes guides discovery of novel xylanolytic species with diverse capacities for hemicellulose hydrolysis.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2021 Jul 2;14(1):150. doi: 10.1186/s13068-021-01995-x. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2021. PMID: 34215291 Free PMC article.
-
Cellulose- and xylan-degrading yeasts: Enzymes, applications and biotechnological potential.Biotechnol Adv. 2022 Oct;59:107981. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2022.107981. Epub 2022 May 14. Biotechnol Adv. 2022. PMID: 35580749 Review.
-
Identification and characterisation of xylanolytic yeasts isolated from decaying wood and sugarcane bagasse in Brazil.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2014 Jun;105(6):1107-19. doi: 10.1007/s10482-014-0172-x. Epub 2014 Apr 19. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2014. PMID: 24748334
-
Towards enzymatic breakdown of complex plant xylan structures: State of the art.Biotechnol Adv. 2016 Nov 15;34(7):1260-1274. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2016.09.001. Epub 2016 Sep 9. Biotechnol Adv. 2016. PMID: 27620948 Review.
Cited by
-
Engineering Saccharomyces cerevisiae for targeted hydrolysis and fermentation of glucuronoxylan through CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing.Microb Cell Fact. 2024 Mar 16;23(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s12934-024-02361-w. Microb Cell Fact. 2024. PMID: 38493086 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic and secretomic analyses of Blastobotrys yeasts reveal key xylanases for biomass decomposition.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025 Aug 1;109(1):175. doi: 10.1007/s00253-025-13556-5. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40748385 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mnich E, Bjarnholt N, Eudes A, Harholt J, Holland C, Jørgensen B, Larsen FH, Liu M, Manat R, Meyer AS, Mikkelsen JD, Motawia MS, Muschiol J, Møller BL, Møller SR, Perzon A, Petersen BL, Ravn JL, Ulvskov P. 2020. Phenolic cross-links: building and de-constructing the plant cell wall. Nat Prod Rep 37:919–961. doi:10.1039/C9NP00028C. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

