Culex tarsalis Is a Competent Host of the Insect-Specific Alphavirus Eilat Virus (EILV)
- PMID: 37098948
- PMCID: PMC10231209
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.01960-22
Culex tarsalis Is a Competent Host of the Insect-Specific Alphavirus Eilat Virus (EILV)
Abstract
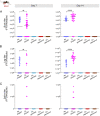
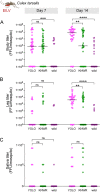
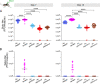
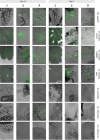
Eilat virus (EILV) is an insect-specific alphavirus that has the potential to be developed into a tool to combat mosquito-borne pathogens. However, its mosquito host range and transmission routes are not well understood. Here, we fill this gap by investigating EILV's host competence and tissue tropism in five mosquito species: Aedes aegypti, Culex tarsalis, Anopheles gambiae, Anopheles stephensi, and Anopheles albimanus. Of the tested species, C. tarsalis was the most competent host for EILV. The virus was found in C. tarsalis ovaries, but no vertical or venereal transmission was observed. Culex tarsalis also transmitted EILV via saliva, suggesting the potential for horizontal transmission between an unknown vertebrate or invertebrate host. We found that reptile (turtle and snake) cell lines were not competent for EILV infection. We tested a potential invertebrate host (Manduca sexta caterpillars) but found they were not susceptible to EILV infection. Together, our results suggest that EILV could be developed as a tool to target pathogenic viruses that use Culex tarsalis as a vector. Our work sheds light on the infection and transmission dynamics of a poorly understood insect-specific virus and reveals it may infect a broader range of mosquito species than previously recognized. IMPORTANCE The recent discovery of insect-specific alphaviruses presents opportunities both to study the biology of virus host range and to develop them into tools against pathogenic arboviruses. Here, we characterize the host range and transmission of Eilat virus in five mosquito species. We find that Culex tarsalis-a vector of harmful human pathogens, including West Nile virus-is a competent host of Eilat virus. However, how this virus is transmitted between mosquitoes remains unclear. We find that Eilat virus infects the tissues necessary for both vertical and horizontal transmission-a crucial step in discerning how Eilat virus maintains itself in nature.
Keywords: Alphavirus; Culex tarsalis; Eilat virus; insect-specific virus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Eilat virus (EILV) causes superinfection exclusion against West Nile virus (WNV) in a strain-specific manner in Culex tarsalis mosquitoes.J Gen Virol. 2024 Aug;105(8):002017. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.002017. J Gen Virol. 2024. PMID: 39189607
-
Eilat virus (EILV) causes superinfection exclusion against West NILE virus (WNV) in a strain specific manner in Culex tarsalis mosquitoes.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 May 25:2023.05.25.542294. doi: 10.1101/2023.05.25.542294. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: J Gen Virol. 2024 Aug;105(8). doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.002017. PMID: 37292979 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Eilat virus displays a narrow mosquito vector range.Parasit Vectors. 2014 Dec 17;7:595. doi: 10.1186/s13071-014-0595-2. Parasit Vectors. 2014. PMID: 25515341 Free PMC article.
-
West Nile Virus Mosquito Vectors in North America.J Med Entomol. 2019 Oct 28;56(6):1475-1490. doi: 10.1093/jme/tjz146. J Med Entomol. 2019. PMID: 31549725 Review.
-
Mosquito Saliva Reshapes Alphavirus Infection and Immunopathogenesis.J Virol. 2018 May 29;92(12):e01004-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01004-17. Print 2018 Jun 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29593049 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transovarial Transmission of Cell-Fusing Agent Virus in Naturally Infected Aedes aegypti Mosquitoes.Viruses. 2024 Jul 11;16(7):1116. doi: 10.3390/v16071116. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39066278 Free PMC article.
-
Agua Salud Alphavirus Infection, Dissemination and Transmission in Aedes aegypti Mosquitoes.Viruses. 2023 May 3;15(5):1113. doi: 10.3390/v15051113. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37243199 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic recovery of Yada Yada virus expands insect-specific alphavirus knowledge and facilitates production of chimeric viruses.Npj Viruses. 2024 Sep 30;2(1):45. doi: 10.1038/s44298-024-00052-2. Npj Viruses. 2024. PMID: 40295870 Free PMC article.
-
Eilat virus (EILV) causes superinfection exclusion against West Nile virus (WNV) in a strain-specific manner in Culex tarsalis mosquitoes.J Gen Virol. 2024 Aug;105(8):002017. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.002017. J Gen Virol. 2024. PMID: 39189607
-
Cell fusing agent virus rarely transmits vertically in artificially infected laboratory-colonized Aedes aegypti mosquitoes.Parasit Vectors. 2024 Apr 4;17(1):177. doi: 10.1186/s13071-024-06232-6. Parasit Vectors. 2024. PMID: 38575981 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pierson TC, Diamond MS. 2013. Flaviviruses, 747–794. In Knipe DM, Howley PM, Cohen JI, Griffin DE, Lamb RA, Martin MA, Racaniello VR, Roizman B (ed), Fields virology. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, MD.
-
- Murray PR, Rosenthal KS, Pfaller MA. 2021. Togaviruses and flaviviruses, 515–526. In Medical microbiology. Elsevier, Amsterdam, Netherlands.
-
- Nasar F, Palacios G, Gorchakov RV, Guzman H, Da Rosa APT, Savji N, Popov VL, Sherman MB, Lipkin WI, Tesh RB, Weaver SC. 2012. Eilat virus, a unique alphavirus with host range restricted to insects by RNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:14622–14627. doi:10.1073/pnas.1204787109. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

