Role of Spillover and Spillback in SARS-CoV-2 Transmission and the Importance of One Health in Understanding the Dynamics of the COVID-19 Pandemic
- PMID: 37098970
- PMCID: PMC10358177
- DOI: 10.1128/jcm.01610-22
Role of Spillover and Spillback in SARS-CoV-2 Transmission and the Importance of One Health in Understanding the Dynamics of the COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
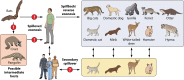
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is notable both for its impact on global public health as well as its well-publicized transmissibility to other species of animals. Infection of incidental animal hosts is concerning because of possible emergence of novel variants due to viral mutation. Species that are susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 include domestic and nondomestic cats, domestic dogs, white-tailed deer, mink, and golden hamsters, among others. We detail possible origins of transmission of SARS-CoV-2 to humans, as well as the ecological and molecular mechanisms needed for the virus to establish infection in humans from animals. We highlight examples of SARS-CoV-2 spillover, spillback, and secondary spillover, demonstrating the breadth in the variability of hosts and current transmission events that have been documented in domestic, captive, and wild animals. Lastly, we turn our focus to the importance of animal hosts as potential reservoirs and sources of variant emergence that can have profound effects on the human population. We note that a One Health approach emphasizing surveillance of animals and humans in certain environments using interdisciplinary collaboration is encouraged to manage disease surveillance, regulation on animal trade and testing, and animal vaccine development that will mitigate further disease outbreaks. These efforts will minimize the spread of SARS-CoV-2 and advance knowledge to prevent the spread of future emerging infectious diseases.
Keywords: One Health; SARS-CoV-2; animals; spillover; veterinary microbiology; zoonoses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wu F, Zhao S, Yu B, Chen Y-M, Wang W, Song Z-G, Hu Y, Tao Z-W, Tian J-H, Pei Y-Y, Yuan M-L, Zhang Y-L, Dai F-H, Liu Y, Wang Q-M, Zheng J-J, Xu L, Holmes EC, Zhang Y-Z. 2020. A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature 579:265–269. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2008-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Munir K, Ashraf S, Munir I, Khalid H, Muneer MA, Mukhtar N, Amin S, Ashraf S, Imran MA, Chaudhry U, Zaheer MU, Arshad M, Munir R, Ahmad A, Zhao X. 2020. Zoonotic and reverse zoonotic events of SARS-CoV-2 and their impact on global health. Emerg Microbes Infect 9:2222–2235. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2020.1827984. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous