SYVN1 ubiquitinates FoxO1 to induce β-catenin nuclear translocation, PD-L1-mediated metastasis, and immune evasion of hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 37099251
- PMCID: PMC10618324
- DOI: 10.1007/s13402-023-00811-y
SYVN1 ubiquitinates FoxO1 to induce β-catenin nuclear translocation, PD-L1-mediated metastasis, and immune evasion of hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: A high incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most frequently diagnosed form of liver cancer, is observed in Africa and Asia. SYVN1 is upregulated in HCC; however, the biological roles of SYVN1 in immune evasion remain unclear.
Methods: RT-qPCR and western blot were employed to detect the expression levels of SYVN1 and the key molecules in HCC cells and tissues. Flow cytometry was used to determine the proportion of T cells, and an ELISA assay was used to determine the amount of IFN-γ secreted. Cell viability was monitored by CCK-8 and colony formation assays. The metastatic properties of HCC cells were detected by Transwell assays. Bioinformatics analysis, ChIP, and luciferase assays were used to study the transcriptional regulation of PD-L1. Co-IP was used to detect direct interaction between SYVN1 and FoxO1, as well as the ubiquitination of FoxO1. The in vitro findings were validated in xenograft and lung metastasis models.
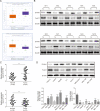
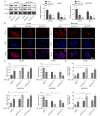
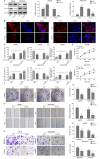
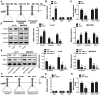
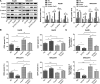
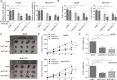
Results: In HCC cells and tissues, SYVN1 was upregulated while FoxO1 was downregulated. SYVN1 knockdown or FoxO1 overexpression reduced PD-L1 expression, and inhibited immune evasion, cell growth, and metastasis in HCC cells. Mechanistically, FoxO1 regulated PD-L1 transcription in a β-catenin-independent or -dependent manner. Functional studies further showed that SYVN1 promoted immune evasion, cell proliferation, migration and invasion via facilitating ubiquitin-proteasome-dependent degradation of FoxO1. In vivo investigations showed that silencing of SYVN1 inhibited immune evasion and metastasis of HCC cells, possible via the FoxO1/PD-L1 axis.
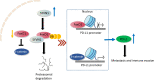
Conclusion: SYVN1 regulates FoxO1 ubiquitination to stimulate β-catenin nuclear translocation and promotes PD-L1-mediated metastasis and immune evasion in HCC.
Keywords: E3 ubiquitin ligase SYVN1; FoxO1; Hepatocellular carcinoma; PD-L1; β-catenin.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
NUAK1 acts as a novel regulator of PD-L1 via activating GSK-3β/β-catenin pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma.Mol Med. 2025 Feb 3;31(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s10020-025-01088-7. Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 39901136 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative proteomics reveals the role of E3 ubiquitin ligase SYVN1 in hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2021 Oct;41(10):1007-1023. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12192. Epub 2021 Jul 1. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2021. PMID: 34196494 Free PMC article.
-
FAT10 induces immune suppression by upregulating PD-L1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma.Apoptosis. 2024 Oct;29(9-10):1529-1545. doi: 10.1007/s10495-024-01982-1. Epub 2024 Jun 2. Apoptosis. 2024. PMID: 38824477
-
Role and therapeutic potential of E3s in the tumor microenvironment of hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 31;15:1483721. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1483721. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39544935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
E3 ubiquitin ligase SYVN1 as a promising therapeutic target for diverse human diseases.Pharmacol Res. 2025 Feb;212:107603. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2025.107603. Epub 2025 Jan 14. Pharmacol Res. 2025. PMID: 39818260 Review.
Cited by
-
Dynamic ubiquitination networks in liver cancer: decoding E3 ligases and deubiquitinases as gatekeepers of therapeutic resistance.Med Oncol. 2025 Jul 20;42(8):352. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02912-0. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40684404 Review.
-
The current status and future of PD-L1 in liver cancer.Front Immunol. 2023 Dec 12;14:1323581. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1323581. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38155974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acetylated KIAA1429 by TIP60 facilitates metastasis and immune evasion of hepatocellular carcinoma via N6-methyladenosine-KDM5B-mediated regulation of FoxO1.Cell Death Discov. 2025 Apr 29;11(1):210. doi: 10.1038/s41420-025-02462-4. Cell Death Discov. 2025. PMID: 40301310 Free PMC article.
-
5,7,4'-Trimethoxyflavone triggers cancer cell PD-L1 ubiquitin-proteasome degradation and facilitates antitumor immunity by targeting HRD1.MedComm (2020). 2024 Jun 27;5(7):e611. doi: 10.1002/mco2.611. eCollection 2024 Jul. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 38938284 Free PMC article.
-
Dihydrotanshinone I Targets PGAM1 to Induce SYVN1-Mediated Ubiquitination and Suppress Glycolysis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Phytother Res. 2025 Aug;39(8):3762-3783. doi: 10.1002/ptr.70017. Epub 2025 Jul 10. Phytother Res. 2025. PMID: 40640077 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

