An accessible infrastructure for artificial intelligence using a Docker-based JupyterLab in Galaxy
- PMID: 37099385
- PMCID: PMC10132306
- DOI: 10.1093/gigascience/giad028
An accessible infrastructure for artificial intelligence using a Docker-based JupyterLab in Galaxy
Abstract
Background: Artificial intelligence (AI) programs that train on large datasets require powerful compute infrastructure consisting of several CPU cores and GPUs. JupyterLab provides an excellent framework for developing AI programs, but it needs to be hosted on such an infrastructure to enable faster training of AI programs using parallel computing.
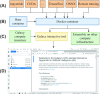
Findings: An open-source, docker-based, and GPU-enabled JupyterLab infrastructure is developed that runs on the public compute infrastructure of Galaxy Europe consisting of thousands of CPU cores, many GPUs, and several petabytes of storage to rapidly prototype and develop end-to-end AI projects. Using a JupyterLab notebook, long-running AI model training programs can also be executed remotely to create trained models, represented in open neural network exchange (ONNX) format, and other output datasets in Galaxy. Other features include Git integration for version control, the option of creating and executing pipelines of notebooks, and multiple dashboards and packages for monitoring compute resources and visualization, respectively.
Conclusions: These features make JupyterLab in Galaxy Europe highly suitable for creating and managing AI projects. A recent scientific publication that predicts infected regions in COVID-19 computed tomography scan images is reproduced using various features of JupyterLab on Galaxy Europe. In addition, ColabFold, a faster implementation of AlphaFold2, is accessed in JupyterLab to predict the 3-dimensional structure of protein sequences. JupyterLab is accessible in 2 ways-one as an interactive Galaxy tool and the other by running the underlying Docker container. In both ways, long-running training can be executed on Galaxy's compute infrastructure. Scripts to create the Docker container are available under MIT license at https://github.com/usegalaxy-eu/gpu-jupyterlab-docker.
Keywords: CUDA; Elyra AI; GPU; Galaxy Europe; JupyterLab; ONNX; artificial intelligence; remote model training.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press GigaScience.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Transformer-based tool recommendation system in Galaxy.BMC Bioinformatics. 2023 Nov 27;24(1):446. doi: 10.1186/s12859-023-05573-w. BMC Bioinformatics. 2023. PMID: 38012574 Free PMC article.
-
Tool recommender system in Galaxy using deep learning.Gigascience. 2021 Jan 6;10(1):giaa152. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/giaa152. Gigascience. 2021. PMID: 33404053 Free PMC article.
-
Expanding the Galaxy's reference data.Bioinform Adv. 2022 Apr 29;2(1):vbac030. doi: 10.1093/bioadv/vbac030. eCollection 2022. Bioinform Adv. 2022. PMID: 35669346 Free PMC article.
-
New and emerging technology for adult social care - the example of home sensors with artificial intelligence (AI) technology.Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2023 Jun;11(9):1-64. doi: 10.3310/HRYW4281. Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2023. PMID: 37470136
-
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE IN MEDICAL PRACTICE: REGULATIVE ISSUES AND PERSPECTIVES.Wiad Lek. 2020;73(12 cz 2):2722-2727. Wiad Lek. 2020. PMID: 33611272 Review.
References
-
- Pearson W, Crusoe M, et al. The FASTA package—protein and DNA sequence similarity searching and alignment programs. GitHub. 2016. https://github.com/wrpearson/fasta36. [Accessed June 30, 2022].
-
- Kumar I, Singh SP, Shivam. Machine learning in bioinformatics. Bioinformatics, Dev BS and Pathak RK , Academic Press; Dehradun 2022:443–56.. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780323897754000201.
-
- Kluyver T, Ragan-Kelley B, Pérez F, Granger B, Bussonnier M, et al. Jupyter Notebooks—A Publishing Format for Reproducible Computational Workflows. IOS Press; Amsterdam. 2016:87.
-
- Kumar A. Container for machine learning and deep learning in Jupyter notebook. Docker. 2021. https://hub.docker.com/r/anupkumar/docker-ml-jupyterlab. [Accessed June 29, 2022]
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

