Profiling Plant Proteome and Transcriptome Changes during Grapevine Fanleaf Virus Infection
- PMID: 37099450
- PMCID: PMC10243147
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.3c00069
Profiling Plant Proteome and Transcriptome Changes during Grapevine Fanleaf Virus Infection
Abstract
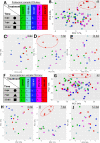
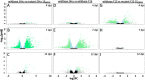
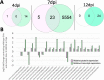
Viruses can elicit varying types and severities of symptoms during plant host infection. We investigated changes in the proteome and transcriptome of Nicotiana benthamiana plants infected by grapevine fanleaf virus (GFLV) with an emphasis on vein clearing symptom development. Comparative, time-course liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry and 3' ribonucleic acid sequencing analyses of plants infected by two wildtype GFLV strains, one symptomatic and one asymptomatic, and their asymptomatic mutant strains carrying a single amino acid change in the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRP) were conducted to identify host biochemical pathways involved in viral symptom development. During peak vein clearing symptom display at 7 days post-inoculation (dpi), protein and gene ontologies related to immune response, gene regulation, and secondary metabolite production were overrepresented when contrasting wildtype GFLV strain GHu and mutant GHu-1EK802GPol. Prior to the onset of symptom development at 4 dpi and when symptoms faded away at 12 dpi, protein and gene ontologies related to chitinase activity, hypersensitive response, and transcriptional regulation were identified. This systems biology approach highlighted how a single amino acid of a plant viral RdRP mediates changes to the host proteome (∼1%) and transcriptome (∼8.5%) related to transient vein clearing symptoms and the network of pathways involved in the virus-host arms race.
Keywords: Nicotiana benthamiana; RNA-dependent RNA polymerase; grapevine; nepovirus; proteomics; symptomology; time-course; transcriptomics; virus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
A single viral amino acid shapes the root system architecture of a plant host upon virus infection.BMC Microbiol. 2024 Jul 19;24(1):267. doi: 10.1186/s12866-024-03399-x. BMC Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39030475 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of protein interactions of grapevine fanleaf virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase during infection of Nicotiana benthamiana by affinity purification and tandem mass spectrometry.J Gen Virol. 2021 May;102(5):001607. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.001607. J Gen Virol. 2021. PMID: 34043500 Free PMC article.
-
A strain-specific segment of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of grapevine fanleaf virus determines symptoms in Nicotiana species.J Gen Virol. 2013 Dec;94(Pt 12):2803-2813. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.057646-0. Epub 2013 Oct 2. J Gen Virol. 2013. PMID: 24088345
-
The Identity of a Single Residue of the RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase of Grapevine Fanleaf Virus Modulates Vein Clearing in Nicotiana benthamiana.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2019 Jul;32(7):790-801. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-12-18-0337-R. Epub 2019 May 22. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2019. PMID: 30640575
-
Detection and genetic variation analysis of grapevine fanleaf virus (GFLV) isolates in China.Arch Virol. 2015 Nov;160(11):2661-7. doi: 10.1007/s00705-015-2566-0. Epub 2015 Aug 12. Arch Virol. 2015. PMID: 26264404 Review.
Cited by
-
Variability of plant transcriptomic responses under stress acclimation: a review from high throughput studies.Acta Biochim Pol. 2024 Oct 25;71:13585. doi: 10.3389/abp.2024.13585. eCollection 2024. Acta Biochim Pol. 2024. PMID: 39524930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Emerging Role of Omics-Based Approaches in Plant Virology.Viruses. 2025 Jul 15;17(7):986. doi: 10.3390/v17070986. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40733603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Grapevine Virome of the Don Ampelographic Collection in Russia Has Concealed Five Novel Viruses.Viruses. 2023 Dec 14;15(12):2429. doi: 10.3390/v15122429. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 38140672 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic changes associated with infection of Nicotiana benthamiana plants with tomato ringspot virus (genus Nepovirus) during the acute symptomatic stage and after symptom recovery.PLoS One. 2025 Sep 2;20(9):e0328517. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0328517. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40892828 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the GH19 Chitinase Gene Family in Sea Island Cotton.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Aug 7;47(8):633. doi: 10.3390/cimb47080633. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40864787 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Osterbaan L. J.; Fuchs M. Dynamic Interactions between Plant Viruses and Their Hosts for Symptom Development. J. Plant Pathol. 2019, 101, 885–895. 10.1007/s42161-019-00323-5. - DOI
-
- Zanardo L. G.; de Souza G. B.; Alves M. S. Transcriptomics of Plant–Virus Interactions: A Review. Theor. Exp. Plant Physiol. 2019, 31, 103–125. 10.1007/s40626-019-00143-z. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

