Ataxic speech disorders and Parkinson's disease diagnostics via stochastic embedding of empirical mode decomposition
- PMID: 37099544
- PMCID: PMC10132693
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0284667
Ataxic speech disorders and Parkinson's disease diagnostics via stochastic embedding of empirical mode decomposition
Abstract
Medical diagnostic methods that utilise modalities of patient symptoms such as speech are increasingly being used for initial diagnostic purposes and monitoring disease state progression. Speech disorders are particularly prevalent in neurological degenerative diseases such as Parkinson's disease, the focus of the study undertaken in this work. We will demonstrate state-of-the-art statistical time-series methods that combine elements of statistical time series modelling and signal processing with modern machine learning methods based on Gaussian process models to develop methods to accurately detect a core symptom of speech disorder in individuals who have Parkinson's disease. We will show that the proposed methods out-perform standard best practices of speech diagnostics in detecting ataxic speech disorders, and we will focus the study, particularly on a detailed analysis of a well regarded Parkinson's data speech study publicly available making all our results reproducible. The methodology developed is based on a specialised technique not widely adopted in medical statistics that found great success in other domains such as signal processing, seismology, speech analysis and ecology. In this work, we will present this method from a statistical perspective and generalise it to a stochastic model, which will be used to design a test for speech disorders when applied to speech time series signals. As such, this work is making contributions both of a practical and statistical methodological nature.
Copyright: © 2023 Campi et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
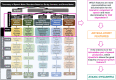
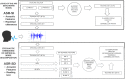



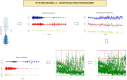

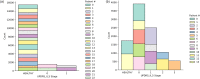




Similar articles
-
Parkinson's disease or atypical parkinsonism? The importance of acoustic voice analysis in differential diagnosis of speech disorders.Brain Behav. 2020 Aug;10(8):e01700. doi: 10.1002/brb3.1700. Epub 2020 Jun 11. Brain Behav. 2020. PMID: 32525283 Free PMC article.
-
Motor speech and non-motor language endophenotypes of Parkinson's disease.Expert Rev Neurother. 2019 Dec;19(12):1191-1200. doi: 10.1080/14737175.2019.1649142. Epub 2019 Aug 8. Expert Rev Neurother. 2019. PMID: 31343928 Review.
-
Discovery of Parkinson's disease states and disease progression modelling: a longitudinal data study using machine learning.Lancet Digit Health. 2021 Sep;3(9):e555-e564. doi: 10.1016/S2589-7500(21)00101-1. Epub 2021 Jul 29. Lancet Digit Health. 2021. PMID: 34334334
-
Fusion of WPT and MFCC feature extraction in Parkinson's disease diagnosis.Technol Health Care. 2019;27(4):363-372. doi: 10.3233/THC-181306. Technol Health Care. 2019. PMID: 30664511
-
[Speech disorders in Parkinson's disease].Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2019;119(9. Vyp. 2):32-36. doi: 10.17116/jnevro201911909232. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2019. PMID: 31825387 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
An automatic measure for speech intelligibility in dysarthrias-validation across multiple languages and neurological disorders.Front Digit Health. 2024 Jul 23;6:1440986. doi: 10.3389/fdgth.2024.1440986. eCollection 2024. Front Digit Health. 2024. PMID: 39108340 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ayaz Z, Naz S, Khan NH, Razzak I, Imran M. Automated methods for diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease and predicting severity level. Neural Computing and Applications. 2022; p. 1–36.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

