Immune response of a two-dose heterologous Ebola vaccine regimen: summary of three African clinical trials using a single validated Filovirus Animal Nonclinical Group enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in a single accredited laboratory
- PMID: 37099841
- PMCID: PMC10149382
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2023.104562
Immune response of a two-dose heterologous Ebola vaccine regimen: summary of three African clinical trials using a single validated Filovirus Animal Nonclinical Group enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in a single accredited laboratory
Abstract
Background: This analysis evaluated the immune response to the two-dose, heterologous Ad26.ZEBOV, MVA-BN-Filo Ebola virus vaccine regimen, administered 56-days apart, from multiple African sites based on results from one analytic laboratory.
Methods: Immunogenicity across three trials (EBL2002, EBL2004/PREVAC, EBL3001) conducted in East and West Africa is summarised. Vaccine-induced Ebola glycoprotein-binding antibody concentrations were analysed by Q2 Solutions laboratory at baseline, 21 days (EBL2002 and EBL3001) or 28 days (EBL2004) post-dose 2 (regimen completion), and 12 months post-dose 1 using the validated Filovirus Animal Nonclinical Group Ebola glycoprotein enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Responders were defined as those with a >2.5-fold increase from baseline or the lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) if <LLOQ at baseline.
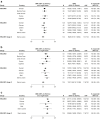
Findings: At 21 or 28 (21/28) days post-dose 2, the geometric mean concentration (GMC) range was 3810-7518 ELISA units (EU)/mL (percent responders: ≥98%) in adults, 9929-13532 EU/mL (≥98%) in adolescents aged 12-17 years, 10,212-17388 EU/mL (≥99%) in older children, and 22,568-25111 EU/mL (≥98%) in younger children. When stratified by country, GMCs at 21/28 days post-dose 2 were generally similar among adults and within paediatric cohorts (percent responders: 95%-100%). At month 12, GMC range was 259-437 EU/mL (percent responders: 49%-88%) in adults and 386-1139 EU/mL (70%-100%) in paediatric participants.
Interpretation: Based on data from a single laboratory using a single validated assay, Ad26.ZEBOV, MVA-BN-Filo induced a strong humoral immune response, with ≥95% of participants across countries classified as responders at 21/28 days post-dose 2 (regimen completion), regardless of age.
Funding: Janssen Vaccines & Prevention BV; Innovative Medicines Initiative.
Keywords: Ad26.ZEBOV; Africa; Ebola; MVA-BN-Filo; Vaccine.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests CM, AG, JH, BK, MD, KL, and CR were full-time employees of Janssen Pharmaceuticals at the time of the study and report stock or stock options in Janssen Pharmaceuticals. HB's institution has received funding from the Innovative Medicines Initiative to conduct the EBL2002 study. M Katwere was a full-time employee of Janssen Pharmaceuticals at the time of the study. SE's institution has received funding from Inserm France to conduct the EBL2002 study. BL's institution has received funding from the Innovative Medicines Initiative to conduct the EBL3005 study. DW-J is a consortia partner with Janssen Pharmaceuticals on EBOVAC1 and EBOVAC3 projects, has received Ad26.MVA Ebola vaccines donated by Janssen Pharmaceuticals for clinical trials under EBOVAC1 and EBOVAC3 projects, and her institution has received funding from the Innovative Medicines Initiative to conduct the EBL3005 study. M Kieh, ZA, BTR, SD, SBS, AS-B, AHB, HK, SBK, OA, MS, EDO, SS, RT, and BG declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . 1976. Ebola virus disease distribution map: cases of Ebola virus disease in Africa since.https://www.cdc.gov/vhf/ebola/history/distribution-map.html
-
- World Health Organization Ebola virus disease. https://www.who.int/health-topics/ebola#tab=tab_1
-
- World Health Organization Ebola virus disease - democratic republic of the Congo. 2022. https://www.who.int/emergencies/disease-outbreak-news/item/2022-DON398
-
- World Health Organization Ebola virus disease – democratic republic of the Congo. 2022. https://www.who.int/emergencies/disease-outbreak-news/item/2022-DON404
-
- World Health Organization Ebola disease caused by Sudan ebolavirus – Uganda. 2023. https://www.who.int/emergencies/disease-outbreak-news/item/2023-DON433
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

