Omicron Spike Protein is Vulnerable to Reduction
- PMID: 37100168
- PMCID: PMC10125213
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2023.168128
Omicron Spike Protein is Vulnerable to Reduction
Abstract
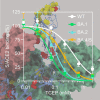
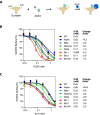
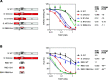
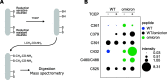
SARS-CoV-2 virus spike (S) protein is an envelope protein responsible for binding to the ACE2 receptor, driving subsequent entry into host cells. The existence of multiple disulfide bonds in the S protein makes it potentially susceptible to reductive cleavage. Using a tri-part split luciferase-based binding assay, we evaluated the impacts of chemical reduction on S proteins from different virus variants and found that those from the Omicron family are highly vulnerable to reduction. Through manipulation of different Omicron mutations, we found that alterations in the receptor binding module (RBM) are the major determinants of this vulnerability. Specifically we discovered that Omicron mutations facilitate the cleavage of C480-C488 and C379-C432 disulfides, which consequently impairs binding activity and protein stability. The vulnerability of Omicron S proteins suggests a mechanism that can be harnessed to treat specific SARS-CoV-2 strains.
Keywords: ACE2; SARS-CoV-2; binding; disulfide; receptor binding motif (RBM).
Copyright © 2023. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Baker J.M., Nakayama J.Y., O’Hegarty M., McGowan A., Teran R.A., Bart S.M., Mosack K., Roberts N., et al. SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (Omicron) Variant Transmission Within Households - Four U.S. Jurisdictions, November 2021-February 2022. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2022;71:341–346. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7109e1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

