Bioactive lipid regulation of platelet function, hemostasis, and thrombosis
- PMID: 37100208
- PMCID: PMC11143998
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2023.108420
Bioactive lipid regulation of platelet function, hemostasis, and thrombosis
Abstract
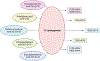
Platelets are small, anucleate cells in the blood that play a crucial role in the hemostatic response but are also implicated in the pathophysiology of cardiovascular disease. It is widely appreciated that polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) play an integral role in the function and regulation of platelets. PUFAs are substrates for oxygenase enzymes cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1), 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX), 12-lipoxygenase (12-LOX) and 15-lipoxygenase (15-LOX). These enzymes generate oxidized lipids (oxylipins) that exhibit either pro- or anti-thrombotic effects. Although the effects of certain oxylipins, such as thromboxanes and prostaglandins, have been studied for decades, only one oxylipin has been therapeutically targeted to treat cardiovascular disease. In addition to the well-known oxylipins, newer oxylipins that demonstrate activity in the platelet have been discovered, further highlighting the expansive list of bioactive lipids that can be used to develop novel therapeutics. This review outlines the known oxylipins, their activity in the platelet, and current therapeutics that target oxylipin signaling.
Keywords: Hemostasis; Oxygenase; Platelet; Prostaglandins; Signal transduction; Thrombosis.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest Dr. Holinstat is a consultant and equity holder for Veralox Therapeutics and Cereno Scientific. All other authors declare no competing interests for this work.
Figures


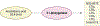

References
-
- Adkins Y, & Kelley DS (2010). Mechanisms underlying the cardioprotective effects of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry 21, 781–792. - PubMed
-
- Anand R, & Kaithwas G (2014). Anti-inflammatory potential of alpha-linolenic acid mediated through selective COX inhibition: Computational and experimental data. Inflammation 37, 1297–1306. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

