Circadian rhythm of hepatic cytosolic and nuclear estrogen and androgen receptors
- PMID: 3710067
- PMCID: PMC2965517
- DOI: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90456-7
Circadian rhythm of hepatic cytosolic and nuclear estrogen and androgen receptors
Abstract
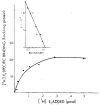
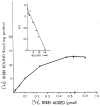
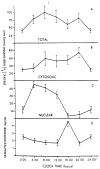
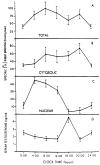
Mammalian liver is a sex steroid-responsive tissue. The effects of these hormones presumably are mediated by hepatic estrogen receptors (ER) and androgen receptors (AR). Serum levels of sex hormones display circadian rhythms. Further, estrogens and androgens are commonly administered; administration of these agents is associated frequently with liver disease. Therefore, we investigated whether the cytosolic and nuclear sex steroid receptors also display a similar circadian rhythm, and whether variations occurred in the distribution of receptors between cytosolic and nuclear compartments. Animals were killed every 4 h from midnight till the following midnight; cytosolic and nuclear levels of both ER and AR were measured. Cytosolic ER reached a maximum level at 4 AM, and a minimum at 8 PM and midnight of both days. Nuclear ER was highest at 8 AM and lowest at 4 PM and 8 PM, a pattern which parallels variations in serum estradiol levels. Cytosolic AR was highest at 8 PM and lowest at midnight and 4 AM. Nuclear AR was highest at 4 AM and lowest at 4 PM and 8 PM. The highest level of nuclear AR does not correspond to the maximum serum testosterone level, which occurred at 4 PM. The total hepatic content of both ER and AR was not constant over the 24-h period, but varied considerably with time of day. These studies suggest that both ER and AR show a distinct circadian rhythm in subcellular compartmentalization, and that total hepatic content of ER and AR varies significantly during a 24-h period.
Figures
References
-
- Eagon PK, Porter LE, Francavilla A, et al. Estrogen and androgen receptors in liver: their role in liver disease and regeneration. Semin Liver Dis. 1985;5:59–69. - PubMed
-
- Corvol PL, Chrambach A, Rodbard D, et al. Physical properties and binding capacity of testosterone-binding globulin in human plasma determined by polyacrylamide electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1971;246:3435–43. - PubMed
-
- Laragh JH, Bauer L, Brunner HR, et al. Renin angiotensin and aldosterone system in pathogenesis and management of hypertensive vascular disease. Am J Med. 1972;52:633–53. - PubMed
-
- Menard J, Corvol P, Foliot A, et al. Effects of estrogens on renin substrate and uterine weights in rats. Endocrinology. 1973;93:747–51. - PubMed
-
- Song CS, Rifkind AB, Gillete PN, et al. The effect of estrogens, progestins and pregnancy on hepatic function. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1969;195:813–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

