Effectiveness of near-UVA in SARS-CoV-2 inactivation
- PMID: 37100744
- PMCID: PMC10203533
- DOI: 10.1017/S0950268823000560
Effectiveness of near-UVA in SARS-CoV-2 inactivation
Abstract
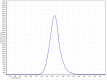
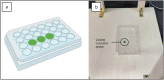
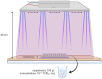
This experimental study aimed to determine the activity of a near-UVA (405 nm) LED ceiling system against the SARS-CoV-2 virus. The ceiling system comprised 17 near-UVA LED lights with a radiant power of 1.1 W/each centred at 405 nm wavelength. A 96-multiwell plate, fixed to a wooden base, was inoculated with suspensions of VERO E6 cell cultures infected with SARS-CoV-2 virus and irradiated at a distance of 40 cm with a dose of 20.2 J/cm2 for 120 min. The collected suspensions were transferred to VERO cell culture plates and incubated for 3 days. The maximum measurable log reduction obtained, starting from a concentration of 107.2 TCID50/mL, was 3.0 log10 and indicated inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 replication by the near-UVA LED ceiling system. Near-UVA light at a 405-nm wavelength is emerging as a potential alternative treatment for localised infections and environmental decontamination because it is far less harmful to living organisms' cells than UV-C irradiation.
Keywords: COVID-19; Cell Colture; Disinfection; Hygiene; Prevention; SARS-CoV-2; UVC; near-UVA; virus infection.
Conflict of interest statement
Ugolini srl partially financed the University of Siena for research and development (R&D) activities related to devices adopting the described technology where G.M. was the principal investigator. R&D led to a patent application owned by Ugolini srl where G.C. and G.M. were co-inventors G.C. and G.M. are co-founders of the company egoHEALTH which was financed by Ugolini srl to cover minor parts of the investigation, included fees for patent activity issues. G.C. and G.M. did not receive any personal funds for the research. Ugolini srl had no role in any part of the manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- COVID-19 Map Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center. Available at https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html (accessed 20 February 2023).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

