A burst of genomic innovation at the origin of placental mammals mediated embryo implantation
- PMID: 37100852
- PMCID: PMC10133327
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-023-04809-y
A burst of genomic innovation at the origin of placental mammals mediated embryo implantation
Abstract
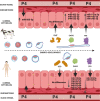
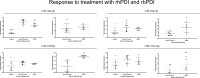
The origin of embryo implantation in mammals ~148 million years ago was a dramatic shift in reproductive strategy, yet the molecular changes that established mammal implantation are largely unknown. Although progesterone receptor signalling predates the origin of mammals and is highly conserved in, and critical for, successful mammal pregnancy, it alone cannot explain the origin and subsequent diversity of implantation strategies throughout the placental mammal radiation. MiRNAs are known to be flexible and dynamic regulators with a well-established role in the pathophysiology of mammal placenta. We propose that a dynamic core microRNA (miRNA) network originated early in placental mammal evolution, responds to conserved mammal pregnancy cues (e.g. progesterone), and facilitates species-specific responses. Here we identify 13 miRNA gene families that arose at the origin of placental mammals and were subsequently retained in all descendent lineages. The expression of these miRNAs in response to early pregnancy molecules is regulated in a species-specific manner in endometrial epithelia of species with extreme implantation strategies (i.e. bovine and human). Furthermore, this set of miRNAs preferentially target proteins under positive selective pressure on the ancestral eutherian lineage. Discovery of this core embryo implantation toolkit and specifically adapted proteins helps explain the origin and evolution of implantation in mammals.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
What was the ancestral function of decidual stromal cells? A model for the evolution of eutherian pregnancy.Placenta. 2016 Apr;40:40-51. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2016.02.012. Epub 2016 Feb 23. Placenta. 2016. PMID: 27016782 Review.
-
Evolution of Embryo Implantation Was Enabled by the Origin of Decidual Stromal Cells in Eutherian Mammals.Mol Biol Evol. 2021 Mar 9;38(3):1060-1074. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msaa274. Mol Biol Evol. 2021. PMID: 33185661 Free PMC article.
-
Progressive Exaptation of Endogenous Retroviruses in Placental Evolution in Cattle.Biomolecules. 2023 Nov 21;13(12):1680. doi: 10.3390/biom13121680. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 38136553 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Origin, evolution, and biological role of miRNA cluster in DLK-DIO3 genomic region in placental mammals.Mol Biol Evol. 2008 May;25(5):939-48. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msn045. Epub 2008 Feb 14. Mol Biol Evol. 2008. PMID: 18281269
-
Phylogenomics and the Genetic Architecture of the Placental Mammal Radiation.Annu Rev Anim Biosci. 2021 Feb 16;9:29-53. doi: 10.1146/annurev-animal-061220-023149. Epub 2020 Nov 23. Annu Rev Anim Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33228377 Review.
Cited by
-
Rapid adaptation of cellular metabolic rate to the MicroRNA complements of mammals and its relevance to the evolution of endothermy.iScience. 2023 Dec 21;27(2):108740. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108740. eCollection 2024 Feb 16. iScience. 2023. PMID: 38327773 Free PMC article.
-
The role of microRNAs in pregnancies complicated by maternal diabetes.Clin Sci (Lond). 2024 Sep 18;138(18):1179-1207. doi: 10.1042/CS20230681. Clin Sci (Lond). 2024. PMID: 39289953 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional response of endometrial cells to Insulin, cultured using microfluidics.Reprod Fertil. 2023 May 1;4(2):e210120. doi: 10.1530/RAF-21-0120. Online ahead of print. Reprod Fertil. 2023. PMID: 37200206 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wagner GP. Evolutionary innovations and novelties: let us get down to business! Zool. Anz. 2015;256:75–81. doi: 10.1016/j.jcz.2015.04.006. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

