Catalytic disconnection of C-O bonds in epoxy resins and composites
- PMID: 37100913
- PMCID: PMC10208972
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-05944-6
Catalytic disconnection of C-O bonds in epoxy resins and composites
Abstract
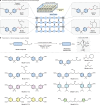
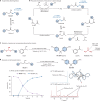
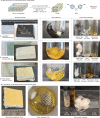
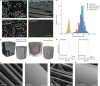
Fibre-reinforced epoxy composites are well established in regard to load-bearing applications in the aerospace, automotive and wind power industries, owing to their light weight and high durability. These composites are based on thermoset resins embedding glass or carbon fibres1. In lieu of viable recycling strategies, end-of-use composite-based structures such as wind turbine blades are commonly landfilled1-4. Because of the negative environmental impact of plastic waste5,6, the need for circular economies of plastics has become more pressing7,8. However, recycling thermoset plastics is no trivial matter1-4. Here we report a transition-metal-catalysed protocol for recovery of the polymer building block bisphenol A and intact fibres from epoxy composites. A Ru-catalysed, dehydrogenation/bond, cleavage/reduction cascade disconnects the C(alkyl)-O bonds of the most common linkages of the polymer. We showcase the application of this methodology to relevant unmodified amine-cured epoxy resins as well as commercial composites, including the shell of a wind turbine blade. Our results demonstrate that chemical recycling approaches for thermoset epoxy resins and composites are achievable.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
A.A., T.S., A.S. and S.F. are inventors on provisional patent application no. EP22156129, submitted by Aarhus University, which covers the transition-metal-catalysed disassembly of epoxy-based, fibre-reinforced, polymer composites. T.S. is co-owner of SyTracks A/S, which commercializes CO tubes.
Figures

References
-
- Navarro CA, et al. A structural chemistry look at composites recycling. Mater. Horiz. 2020;7:2479–2486. doi: 10.1039/D0MH01085E. - DOI
-
- Oliveux G, Dandy LO, Leeke GA. Current status of recycling of fibre reinforced polymers: review of technologies, reuse and resulting properties. Prog. Mater Sci. 2015;72:61–99. doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2015.01.004. - DOI
-
- Witik RA, Teuscher R, Michaud V, Ludwig C, Månson J-AE. Carbon fibre reinforced composite waste: an environmental assessment of recycling, energy recovery and landfilling. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2013;49:89–99. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2013.02.009. - DOI
-
- Jacoby M. Recycling wind turbine blades. C&EN Global Enterprise. 2022;100:26–30. doi: 10.1021/cen-10027-cover. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

