Branched-chain amino acid catabolism in muscle affects systemic BCAA levels but not insulin resistance
- PMID: 37100997
- PMCID: PMC10278155
- DOI: 10.1038/s42255-023-00794-y
Branched-chain amino acid catabolism in muscle affects systemic BCAA levels but not insulin resistance
Abstract
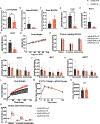
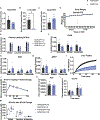
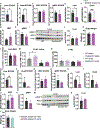
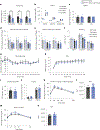
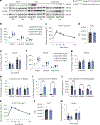
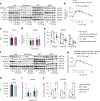
Elevated levels of plasma branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) have been associated with insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes since the 1960s. Pharmacological activation of branched-chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase (BCKDH), the rate-limiting enzyme of BCAA oxidation, lowers plasma BCAAs and improves insulin sensitivity. Here we show that modulation of BCKDH in skeletal muscle, but not liver, affects fasting plasma BCAAs in male mice. However, despite lowering BCAAs, increased BCAA oxidation in skeletal muscle does not improve insulin sensitivity. Our data indicate that skeletal muscle controls plasma BCAAs, that lowering fasting plasma BCAAs is insufficient to improve insulin sensitivity and that neither skeletal muscle nor liver account for the improved insulin sensitivity seen with pharmacological activation of BCKDH. These findings suggest potential concerted contributions of multiple tissues in the modulation of BCAA metabolism to alter insulin sensitivity.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
R.J.R.F. and B.B.Z. are employees of Pfizer. This work was in part supported by Pfizer. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Diabetes and branched-chain amino acids: What is the link?J Diabetes. 2018 May;10(5):350-352. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.12645. Epub 2018 Feb 13. J Diabetes. 2018. PMID: 29369529
-
Branched-chain amino acid metabolism, insulin sensitivity and liver fat response to exercise training in sedentary dysglycaemic and normoglycaemic men.Diabetologia. 2021 Feb;64(2):410-423. doi: 10.1007/s00125-020-05296-0. Epub 2020 Oct 29. Diabetologia. 2021. PMID: 33123769 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial pyruvate carrier inhibition initiates metabolic crosstalk to stimulate branched chain amino acid catabolism.Mol Metab. 2023 Apr;70:101694. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2023.101694. Epub 2023 Feb 18. Mol Metab. 2023. PMID: 36801448 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Effects of BCAAs on Insulin Resistance in Athletes.J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2019;65(5):383-389. doi: 10.3177/jnsv.65.383. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2019. PMID: 31666474 Review.
-
Insulin action, type 2 diabetes, and branched-chain amino acids: A two-way street.Mol Metab. 2021 Oct;52:101261. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2021.101261. Epub 2021 May 24. Mol Metab. 2021. PMID: 34044180 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Toward Systems-Level Metabolic Analysis in Endocrine Disorders and Cancer.Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2023 Dec;38(6):619-630. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2023.1814. Epub 2023 Nov 21. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2023. PMID: 37989266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SGLT2 inhibitors activate pantothenate kinase in the human heart.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 27:2024.07.26.605401. doi: 10.1101/2024.07.26.605401. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39091820 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Disruption of BCAA degradation is a critical characteristic of diabetic cardiomyopathy revealed by integrated transcriptome and metabolome analysis.Open Life Sci. 2024 Dec 31;19(1):20220974. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-0974. eCollection 2024. Open Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39822378 Free PMC article.
-
Towards Metabolomic-Based Precision Approaches for Classifying and Treating Heart Failure.JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2024 Jul 31;9(9):1144-1158. doi: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2024.04.008. eCollection 2024 Sep. JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 39444924 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differences in branched-chain amino acid to tyrosine ratio (BTR) among etiologies of chronic liver disease progression compared to healthy adults.J Gastroenterol. 2024 Jun;59(6):483-493. doi: 10.1007/s00535-024-02092-0. Epub 2024 Mar 26. J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38530472
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Diabetes Statistics Report (CDC, 2020).
-
- Randle PJ, Garland PB, Hales CN & Newsholme EA The glucose fatty-acid cycle. Its role in insulin sensitivity and the metabolic disturbances of diabetes mellitus. Lancet 281, 785–789 (1963). - PubMed
-
- McGarry JD What if Minkowski had been ageusic? An alternative angle on diabetes. Science 258, 766–770 (1992). - PubMed
-
- Shulman GI Ectopic fat in insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and cardiometabolic disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 371, 2236–2238 (2014). - PubMed

