Effects of hormones on intestinal stem cells
- PMID: 37101229
- PMCID: PMC10134583
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-023-03336-1
Effects of hormones on intestinal stem cells
Abstract
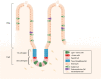
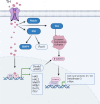
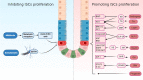
The maintenance of intestinal renewal and repair mainly depends on intestinal stem cells (ISCs), which can also contribute to the growth of intestinal tumours. Hormones, which are vital signalling agents in the body, have various effects on the growth and replacement of intestinal stem cells. This review summarises recent progress in the identification of hormones associated with intestinal stem cells. Several hormones, including thyroid hormone, glucagon-like peptide-2, androgens, insulin, leptin, growth hormone, corticotropin-releasing hormone and progastrin, promote the development of intestinal stem cells. However, somatostatin and melatonin are two hormones that prevent the proliferation of intestinal stem cells. Therefore, new therapeutic targets for the diagnosis and treatment of intestinal illnesses can be identified by examining the impact of hormones on intestinal stem cells.
Keywords: Hormones; Intestinal stem cells; Stem cell; Therapy.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glucagon-Like Peptide-2 Stimulates S-Phase Entry of Intestinal Lgr5+ Stem Cells.Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;13(6):1829-1842. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2022.02.011. Epub 2022 Feb 23. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 35218981 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin/IGF-1 enhances intestinal epithelial crypt proliferation through PI3K/Akt, and not ERK signaling in obese humans.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2018 Jul;243(11):911-916. doi: 10.1177/1535370218785152. Epub 2018 Jun 27. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2018. PMID: 29950119 Free PMC article.
-
Spatio-temporal expression profile of stem cell-associated gene LGR5 in the intestine during thyroid hormone-dependent metamorphosis in Xenopus laevis.PLoS One. 2010 Oct 22;5(10):e13605. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013605. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21042589 Free PMC article.
-
Thyroid hormone regulation of intestinal epithelial stem cell biology.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2017 Dec 25;459:90-97. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2017.03.002. Epub 2017 Mar 10. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 28288904 Review.
-
Effects of Immune Cells on Intestinal Stem Cells: Prospects for Therapeutic Targets.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2022 Oct;18(7):2296-2314. doi: 10.1007/s12015-022-10347-7. Epub 2022 Mar 12. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2022. PMID: 35279803 Review.
Cited by
-
Glucagon-like peptides agonists promote maturation of intestinal organoids derived from neonates with necrotizing enterocolitis.Pediatr Surg Int. 2025 Jan 19;41(1):69. doi: 10.1007/s00383-024-05957-w. Pediatr Surg Int. 2025. PMID: 39828765
-
The Potential Role of Intestinal Stem Cells and Microbiota for the Treatment of Colorectal Cancer.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1470:115-128. doi: 10.1007/5584_2024_803. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 38811486 Review.
-
Evidence of a pan-tissue decline in stemness during human aging.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Apr 4;16(7):5796-5810. doi: 10.18632/aging.205717. Epub 2024 Apr 4. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38604248 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotinamide riboside alleviates ionizing radiation-induced intestinal senescence by alleviating oxidative damage and regulating intestinal metabolism.J Adv Res. 2025 Jun;72:421-432. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.07.010. Epub 2024 Jul 17. J Adv Res. 2025. PMID: 39029900 Free PMC article.
-
Progastrin: An Overview of Its Crucial Role in the Tumorigenesis of Gastrointestinal Cancers.Biomedicines. 2024 Apr 17;12(4):885. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12040885. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38672239 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

