Immunomodulatory effects of modified Liu-Wei-Di-Huang-Wan Traditional Chinese medicine on allergic asthmatic mice
- PMID: 37101296
- PMCID: PMC10134635
- DOI: 10.1186/s13223-023-00792-5
Immunomodulatory effects of modified Liu-Wei-Di-Huang-Wan Traditional Chinese medicine on allergic asthmatic mice
Abstract
Background: Allergic asthma occurs worldwide and is particularly prevalent in westernized countries characterized by chronic airway inflammation resulting in airway hyperresponsiveness. The house dust mites (HDM) including Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus are major sources of sensitization and triggering allergic symptoms in asthmatic patients. The Der p 2 is a major allergen and the predominant source of causative respiratory disorders which induce airway inflammation and bronchial constriction in mite-allergic patients. Few studies evaluate the ameliorating effects of modified Liu-Wei-Di-Huang-Wan (modified LWDHW) on allergic asthma.
Methods: This study aimed to investigate the immunological mechanisms of modified LWDHW on the reductions of airway inflammation, signal transduction, inflammatory cytokine production, Th2 cell proliferation, and bronchial obstruction in Der p 2-induced asthmatic mice.
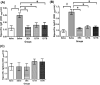
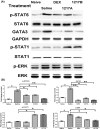
Results: At least ten active ingredients were contained in the formula of modified LWDHW- 1217A and 1217B. Results showed that the immunoglobulin generations (Der p 2 specific- IgE and IgG1), inflammatory cytokine productions (IL-5 and IL-13) in the Sera and BALF could be down-regulated, and the Th1-cytokine productions (IL-12 and IFN-γ) be increased after immunotherapy with modified LWDHW of 1217A or 1217B. The inflammatory cell infiltrations (macrophages, eosinophils, and neutrophils) in the airway and the expressions of TH2-related genes (IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13), TH2-related transcription factor (GATA-3), and neutrophil chemotactic chemokine (IL-8) in the lung tissue of asthmatic mice were significantly decreased after the immunotherapy. The Th1/Th2 polarization had been identified that the IL-4+/CD4+ T cells were downregulated and IFN-γ+/CD4+ T cells were increased. The airway hyperresponsiveness to methacholine inhalation of Penh values was significantly decreased in the treated groups. There were significant improvements in the bronchus histopathology after immunotherapy with 1217A or 1217B which were evaluated by tracheal thickness, inflammatory cell count, and tracheal rupture of mouse lung.
Conclusion: It revealed that 1217A or 1217B could regulate the immune responses and improve pulmonary function. Data suggests that modified LWDHW of 1217A or 1217B have the potential for use as a therapeutic intervention for the treatment of mite allergen Der p 2-induced allergic asthma.
Keywords: Allergic asthma; Der p 2; Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus; House dust mite; Immunotherapy; Liu-Wei-Di-Huang-Wan (LWDHW).
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Der p 2.1 Peptide Abrogates House Dust Mites-Induced Asthma Features in Mice and Humanized Mice by Inhibiting DC-Mediated T Cell Polarization.Front Immunol. 2020 Nov 18;11:565431. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.565431. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33312170 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of liu-wei-di-huang wan on cytokine gene expression from human peripheral blood lymphocytes.Am J Chin Med. 2003;31(2):247-57. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X03000886. Am J Chin Med. 2003. PMID: 12856863
-
Effects of Local Nasal Immunotherapy with FIP-fve Peptide and Denatured Tyrophagus putrescentiae for Storage Mite-Induced Airway Inflammation.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2022 Jan 31;70(1):6. doi: 10.1007/s00005-022-00645-w. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2022. PMID: 35099617
-
Der p 1 and Der p 2 induce less severe late asthmatic responses than native Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus extract after a similar early asthmatic response.Clin Exp Allergy. 2001 May;31(5):705-14. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2222.2001.01120.x. Clin Exp Allergy. 2001. PMID: 11422129 Clinical Trial.
-
Allergic and nonallergic interactions between house dust mite allergens and airway mucosa.Eur Respir J. 1997 Mar;10(3):719-26. Eur Respir J. 1997. PMID: 9073012 Review.
References
-
- Venter C, Palumbo MP, Sauder KA, Glueck DH, Liu AH, Yang IV, et al. Incidence and timing of offspring asthma, wheeze, allergic rhinitis, atopic dermatitis, and food allergy and association with maternal history of asthma and allergic rhinitis. World Allergy Organ J. 2021;14(3):100526. doi: 10.1016/j.waojou.2021.100526. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Luskin AT, Chipps BE, Rasouliyan L, Miller DP, Haselkorn T, Dorenbaum A. Impact of asthma exacerbations and asthma triggers on asthma-related quality of life in patients with severe or difficult-to-treat asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2014;2(5):544–552. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2014.02.011. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

