Early Changes of Serum Interleukin 14α Levels Predicts the Response to Anti-PD-1 Therapy in Cancer
- PMID: 37101524
- PMCID: PMC10123909
- DOI: 10.1177/11795549231163369
Early Changes of Serum Interleukin 14α Levels Predicts the Response to Anti-PD-1 Therapy in Cancer
Abstract
Background: Programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) blockade has been shown to confer clinical benefit in cancer patients. Here, we assessed the level of serum interleukin 14α (IL14α) in patients receiving anti-PD-1 treatment.
Methods: This prospective study recruited 30 patients with advanced solid cancer who received pembrolizumab treatment in Northern Jiangsu People's Hospital between April 2016 and June 2018. The western blot analysis was used to assess the expression level of serum IL14α in patients at baseline and after 2 cycles of treatment. Interleukin 14α was performed using the unpaired 2-tailed Student test. The progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were calculated using the Kaplan-Meier method and compared by the log-rank test.
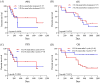
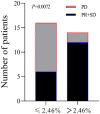
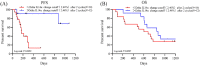
Results: The early change of IL14α after 2 cycles of anti-PD-1 therapy was calculated as delta IL14α % change = (IL14α level after 2 cycles - IL14α level before treatment)/IL14α level before treatment × 100%. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) was analyzed to get a cutoff point of delta IL14α % change as 2.46% (sensitivity = 85.71%, specificity = 62.5%; area under the ROC curve [AUC] = 0.7277, P = .034). Using this cutoff to subgroup the patients, an improved objective response rate was observed in patients with a delta IL14α change higher than 2.46% (P = .0072). A delta IL14α change over 2.46% was associated with a superior PFS (P = .0039).
Conclusions: Early changes of serum IL14α levels may be a promising biomarker to predict outcomes in patients with solid cancer following anti-PD-1 treatment.
Keywords: Interleukin 14α; cancer; prognosis; programmed cell death-1 inhibitor.
© The Author(s) 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Association of Survival and Immune-Related Biomarkers With Immunotherapy in Patients With Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Meta-analysis and Individual Patient-Level Analysis.JAMA Netw Open. 2019 Jul 3;2(7):e196879. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.6879. JAMA Netw Open. 2019. PMID: 31290993 Free PMC article.
-
Baseline Serum Cholesterol Levels Predict the Response of Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Based Treatment.Cancer Manag Res. 2021 May 18;13:4041-4053. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S304022. eCollection 2021. Cancer Manag Res. 2021. PMID: 34040444 Free PMC article.
-
The lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio could predict the efficacy of PD-1 inhibitors in patients with advanced cancer.Transl Cancer Res. 2020 Jul;9(7):4111-4120. doi: 10.21037/tcr-20-1451. Transl Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 35117780 Free PMC article.
-
Pembrolizumab for Previously Treated Advanced or Metastatic Urothelial Cancer: An Evidence Review Group Perspective of a NICE Single Technology Appraisal.Pharmacoeconomics. 2019 Jan;37(1):19-27. doi: 10.1007/s40273-018-0689-3. Pharmacoeconomics. 2019. PMID: 30030817 Review.
-
Predictive Values of Programmed Cell Death-Ligand 1 Expression for Prognosis, Clinicopathological Factors, and Response to Programmed Cell Death-1/Programmed Cell Death-Ligand 1 Inhibitors in Patients With Gynecological Cancers: A Meta-Analysis.Front Oncol. 2021 Feb 1;10:572203. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.572203. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33634012 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

