DEEPCYPs: A deep learning platform for enhanced cytochrome P450 activity prediction
- PMID: 37101544
- PMCID: PMC10123292
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1099093
DEEPCYPs: A deep learning platform for enhanced cytochrome P450 activity prediction
Abstract
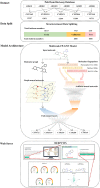
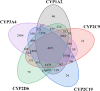
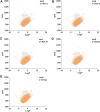
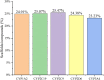
Cytochrome P450 (CYP) is a superfamily of heme-containing oxidizing enzymes involved in the metabolism of a wide range of medicines, xenobiotics, and endogenous compounds. Five of the CYPs (1A2, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, and 3A4) are responsible for metabolizing the vast majority of approved drugs. Adverse drug-drug interactions, many of which are mediated by CYPs, are one of the important causes for the premature termination of drug development and drug withdrawal from the market. In this work, we reported in silicon classification models to predict the inhibitory activity of molecules against these five CYP isoforms using our recently developed FP-GNN deep learning method. The evaluation results showed that, to the best of our knowledge, the multi-task FP-GNN model achieved the best predictive performance with the highest average AUC (0.905), F1 (0.779), BA (0.819), and MCC (0.647) values for the test sets, even compared to advanced machine learning, deep learning, and existing models. Y-scrambling testing confirmed that the results of the multi-task FP-GNN model were not attributed to chance correlation. Furthermore, the interpretability of the multi-task FP-GNN model enables the discovery of critical structural fragments associated with CYPs inhibition. Finally, an online webserver called DEEPCYPs and its local version software were created based on the optimal multi-task FP-GNN model to detect whether compounds bear potential inhibitory activity against CYPs, thereby promoting the prediction of drug-drug interactions in clinical practice and could be used to rule out inappropriate compounds in the early stages of drug discovery and/or identify new CYPs inhibitors.
Keywords: CYPs inhibitors; cytochrome P450; deep learning; multi-task FP-GNN; online webserver.
Copyright © 2023 Ai, Cai, Wei, Zhao, Chen and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A multi-task FP-GNN framework enables accurate prediction of selective PARP inhibitors.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 11;13:971369. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.971369. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36304149 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing machine learning to predict cytochrome P450 inhibition through molecular properties.Arch Toxicol. 2024 Aug;98(8):2647-2658. doi: 10.1007/s00204-024-03756-9. Epub 2024 Apr 15. Arch Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38619593
-
Computational Prediction of Inhibitors and Inducers of the Major Isoforms of Cytochrome P450.Molecules. 2022 Sep 10;27(18):5875. doi: 10.3390/molecules27185875. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36144612 Free PMC article.
-
iCYP-MFE: Identifying Human Cytochrome P450 Inhibitors Using Multitask Learning and Molecular Fingerprint-Embedded Encoding.J Chem Inf Model. 2022 Nov 14;62(21):5059-5068. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.1c00628. Epub 2021 Oct 21. J Chem Inf Model. 2022. PMID: 34672553 Review.
-
Cytochrome P450 enzymes in drug metabolism: regulation of gene expression, enzyme activities, and impact of genetic variation.Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Apr;138(1):103-41. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2012.12.007. Epub 2013 Jan 16. Pharmacol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23333322 Review.
Cited by
-
Advancing ADMET prediction for major CYP450 isoforms: graph-based models, limitations, and future directions.Biomed Eng Online. 2025 Jul 23;24(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s12938-025-01412-6. Biomed Eng Online. 2025. PMID: 40702475 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MEN: leveraging explainable multimodal encoding network for precision prediction of CYP450 inhibitors.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):21820. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-04982-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40592952 Free PMC article.
-
Decoding the Role of CYP450 Enzymes in Metabolism and Disease: A Comprehensive Review.Biomedicines. 2024 Jul 2;12(7):1467. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12071467. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39062040 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pyrazoline B-Paclitaxel or Doxorubicin Combination Drugs Show Synergistic Activity Against Cancer Cells: In silico Study.Adv Appl Bioinform Chem. 2024 Feb 27;17:33-46. doi: 10.2147/AABC.S452281. eCollection 2024. Adv Appl Bioinform Chem. 2024. PMID: 38435441 Free PMC article.
-
Employing Automated Machine Learning (AutoML) Methods to Facilitate the In Silico ADMET Properties Prediction.J Chem Inf Model. 2025 Apr 14;65(7):3215-3225. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.4c02122. Epub 2025 Mar 14. J Chem Inf Model. 2025. PMID: 40085003 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

