Anatomical variability of kidney arterial vasculature based on zonal and segmental topography
- PMID: 37101622
- PMCID: PMC10123188
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15315
Anatomical variability of kidney arterial vasculature based on zonal and segmental topography
Abstract
Introduction: To date, there is no unified approach to the lobar, zonal, and segmental structure of the kidney vasculature. There is no recognizable approach to define basic characteristics in regard to the lobes and segments identifying of the kidney. The branching of the renal artery has often been the subject of scientific research. This study aimed to analyze the arterial anatomy on the basis of zonal and segmental topography.
Materials and methods: This study is a prospective cadaver study on autopsy material using corrosion casting and CT imaging techniques. The arterial vasculature was visualized using corrosive casting. In this study, 116 vascular casts were included. We identified the number of arteries in the kidney hilum, their topography, branching variations of the renal artery, and local blood supply zones of renal masses considering second- and third-order renal artery branches. We used a micro-CT BRUKER SkyScan 1178, digital camera, Mimics-8.1, and R.
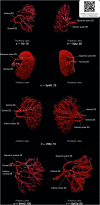
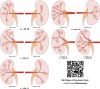
Results: This study has shown that RA divides into two or three zonal arteries, forming a two- or three-zonal vascular supply system. In the case of the two-zonal system, 54.3% of cases accounted for RA branching into ventral and dorsal arteries, whereas 15.5% of cases referred to superior polar and inferior polar zonal arteries. The three-zonal system implies 4 types of RA branching: 1) superior polar, ventral, and dorsal zonal branches (12.9%); 2) ventral, dorsal, and inferior polar zonal branches (9.5%); 3) two ventral and one dorsal zonal branches (5.2%), and 4) superior polar, central, and inferior polar zonal branches (2.5%).
Conclusions: The results of this research make us reconsider Grave's classification theory.
Keywords: Renal segments; Segmental renal arteries; Zonal arteries.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Anatomical study of renal arterial vasculature and its potential impact on partial nephrectomy.BJU Int. 2017 Jul;120(1):83-91. doi: 10.1111/bju.13788. Epub 2017 Feb 20. BJU Int. 2017. PMID: 28117559
-
Comprehensive Study of Arrangement of Renal Hilar Structures and Branching Pattern of Segmental Renal Arteries: An Anatomical Study.Cureus. 2023 Jul 19;15(7):e42165. doi: 10.7759/cureus.42165. eCollection 2023 Jul. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37602117 Free PMC article.
-
Dog kidney: anatomical relationships between intrarenal arteries and kidney collecting system.Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2007 Aug;290(8):1017-22. doi: 10.1002/ar.20567. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2007. PMID: 17654675
-
Morphological variability of the renal artery branching pattern: a brief review and an anatomical study.Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2012;53(2):287-91. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2012. PMID: 22732797 Review.
-
Bilateral prehilar multiple branching of renal arteries: a case report and literature review.Kathmandu Univ Med J (KUMJ). 2006 Jul-Sep;4(3):345-8. Kathmandu Univ Med J (KUMJ). 2006. PMID: 18603933 Review.
Cited by
-
Early-Branched Short Renal Arteries Are False Multiple Renal Arteries.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Apr 20;15(8):1046. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15081046. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40310429 Free PMC article.
-
Approaches to vascular network, blood flow, and metabolite distribution modeling in brain tissue.Biophys Rev. 2023 Aug 18;15(5):1335-1350. doi: 10.1007/s12551-023-01106-0. eCollection 2023 Oct. Biophys Rev. 2023. PMID: 37974995 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

