Toxin-antitoxin systems in bacterial pathogenesis
- PMID: 37101643
- PMCID: PMC10123168
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14220
Toxin-antitoxin systems in bacterial pathogenesis
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "Toxin-antitoxin systems in bacterial pathogenesis" [Heliyon Volume 9, Issue 4, April 2023, Article e14220].Heliyon. 2025 Feb 25;11(4):e42945. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e42945. eCollection 2025 Feb 28. Heliyon. 2025. PMID: 40201281 Free PMC article.
Abstract
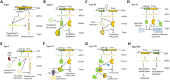
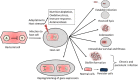
Toxin-Antitoxin (TA) systems are abundant in prokaryotes and play an important role in various biological processes such as plasmid maintenance, phage inhibition, stress response, biofilm formation, and dormant persister cell generation. TA loci are abundant in pathogenic intracellular micro-organisms and help in their adaptation to the harsh host environment such as nutrient deprivation, oxidation, immune response, and antimicrobials. Several studies have reported the involvement of TA loci in establishing successful infection, intracellular survival, better colonization, adaptation to host stresses, and chronic infection. Overall, the TA loci play a crucial role in bacterial virulence and pathogenesis. Nonetheless, there are some controversies about the role of TA system in stress response, biofilm and persister formation. In this review, we describe the role of the TA systems in bacterial virulence. We discuss the important features of each type of TA system and the recent discoveries identifying key contributions of TA loci in bacterial pathogenesis.
Keywords: Biofilm formation; Host stress; Infection; Intracellular survival; Toxin-antitoxin; Virulence.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

