Bioinspired Lipid Nanocarriers for RNA Delivery
- PMID: 37101812
- PMCID: PMC10125326
- DOI: 10.1021/acsbiomedchemau.2c00073
Bioinspired Lipid Nanocarriers for RNA Delivery
Abstract
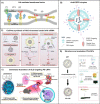
RNA therapy is a disruptive technology comprising a rapidly expanding category of drugs. Further translation of RNA therapies to the clinic will improve the treatment of many diseases and help enable personalized medicine. However, in vivo delivery of RNA remains challenging due to the lack of appropriate delivery tools. Current state-of-the-art carriers such as ionizable lipid nanoparticles still face significant challenges, including frequent localization to clearance-associated organs and limited (1-2%) endosomal escape. Thus, delivery vehicles must be improved to further unlock the full potential of RNA therapeutics. An emerging strategy is to modify existing or new lipid nanocarriers by incorporating bioinspired design principles. This method generally aims to improve tissue targeting, cellular uptake, and endosomal escape, addressing some of the critical issues facing the field. In this review, we introduce the different strategies for creating bioinspired lipid-based RNA carriers and discuss the potential implications of each strategy based on reported findings. These strategies include incorporating naturally derived lipids into existing nanocarriers and mimicking bioderived molecules, viruses, and exosomes. We evaluate each strategy based on the critical factors required for delivery vehicles to succeed. Finally, we point to areas of research that should be furthered to enable the more successful rational design of lipid nanocarriers for RNA delivery.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Endosomal escape mechanisms of extracellular vesicle-based drug carriers: lessons for lipid nanoparticle design.Extracell Vesicles Circ Nucl Acids. 2024 Jul 5;5(3):344-357. doi: 10.20517/evcna.2024.19. eCollection 2024. Extracell Vesicles Circ Nucl Acids. 2024. PMID: 39697635 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid-Based Nanocarriers for RNA Delivery.Curr Pharm Des. 2015;21(22):3140-7. doi: 10.2174/1381612821666150531164540. Curr Pharm Des. 2015. PMID: 26027572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The engineering challenges and opportunities when designing potent ionizable materials for the delivery of ribonucleic acids.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2022 Dec;19(12):1650-1663. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2022.2144827. Epub 2022 Nov 21. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2022. PMID: 36377494 Review.
-
Lipid-based nanoparticles for siRNA delivery in cancer therapy: paradigms and challenges.Acc Chem Res. 2012 Jul 17;45(7):1163-71. doi: 10.1021/ar300048p. Epub 2012 May 8. Acc Chem Res. 2012. PMID: 22568781
-
Lipid Nanoparticle Technology for Clinical Translation of siRNA Therapeutics.Acc Chem Res. 2019 Sep 17;52(9):2435-2444. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00368. Epub 2019 Aug 9. Acc Chem Res. 2019. PMID: 31397996 Review.
Cited by
-
The multifaceted roles of circular RNAs in cancer hallmarks: From mechanisms to clinical implications.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024 Jul 20;35(3):102286. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2024.102286. eCollection 2024 Sep 10. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024. PMID: 39188305 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights on Natural Membrane Characterization for the Rational Design of Biomimetic Drug Delivery Systems.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Jun 27;17(7):841. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17070841. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40733051 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicle mimetics as delivery vehicles for oligonucleotide-based therapeutics and plasmid DNA.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Oct 17;12:1437817. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1437817. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39493304 Free PMC article.
-
Delivery strategies for RNA-targeting therapeutic nucleic acids and RNA-based vaccines against respiratory RNA viruses: IAV, SARS-CoV-2, RSV.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2025 May 20;36(3):102572. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2025.102572. eCollection 2025 Sep 9. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2025. PMID: 40529300 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Berberine hydrochloride-loaded liposomes-in-hydrogel microneedles achieve the efficient treatment for psoriasis.Mater Today Bio. 2025 Apr 25;32:101795. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.101795. eCollection 2025 Jun. Mater Today Bio. 2025. PMID: 40343170 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jackson L. A.; Anderson E. J.; Rouphael N. G.; Roberts P. C.; Makhene M.; Coler R. N.; McCullough M. P.; Chappell J. D.; Denison M. R.; Stevens L. J.; et al. An mRNA Vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 — Preliminary Report. New England Journal of Medicine 2020, 383 (20), 1920–1931. 10.1056/NEJMoa2022483. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Adams D.; Gonzalez-Duarte A.; O’Riordan W. D.; Yang C.-C.; Ueda M.; Kristen A. V.; Tournev I.; Schmidt H. H.; Coelho T.; Berk J. L.; et al. Patisiran, an RNAi Therapeutic, for Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis. New England Journal of Medicine 2018, 379 (1), 11–21. 10.1056/NEJMoa1716153. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

