Data-Driven Elucidation of Flavor Chemistry
- PMID: 37102791
- PMCID: PMC10176570
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c00909
Data-Driven Elucidation of Flavor Chemistry
Abstract
Flavor molecules are commonly used in the food industry to enhance product quality and consumer experiences but are associated with potential human health risks, highlighting the need for safer alternatives. To address these health-associated challenges and promote reasonable application, several databases for flavor molecules have been constructed. However, no existing studies have comprehensively summarized these data resources according to quality, focused fields, and potential gaps. Here, we systematically summarized 25 flavor molecule databases published within the last 20 years and revealed that data inaccessibility, untimely updates, and nonstandard flavor descriptions are the main limitations of current studies. We examined the development of computational approaches (e.g., machine learning and molecular simulation) for the identification of novel flavor molecules and discussed their major challenges regarding throughput, model interpretability, and the lack of gold-standard data sets for equitable model evaluation. Additionally, we discussed future strategies for the mining and designing of novel flavor molecules based on multi-omics and artificial intelligence to provide a new foundation for flavor science research.
Keywords: active ingredients; bioinformatics; cheminformatics; database; machine learning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
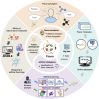



References
-
- Eelager M. P.; Masti S. P.; Chougale R. B.; Hiremani V. D.; Narasgoudar S. S.; Dalbanjan N. P.; S.K. P. K. Evaluation of mechanical, antimicrobial, and antioxidant properties of vanillic acid induced chitosan/poly (vinyl alcohol) active films to prolong the shelf life of green chilli. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 232, 123499.10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.123499. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhang D.; Ouyang S.; Cai M.; Zhang H.; Ding S.; Liu D.; Cai P.; Le Y.; Hu Q. N. FADB-China: A molecular-level food adulteration database in China based on molecular fingerprints and similarity algorithms prediction expansion. Food Chem. 2020, 327, 127010.10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127010. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

