Advances in Nanogels for Topical Drug Delivery in Ocular Diseases
- PMID: 37102904
- PMCID: PMC10137933
- DOI: 10.3390/gels9040292
Advances in Nanogels for Topical Drug Delivery in Ocular Diseases
Abstract
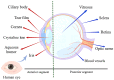
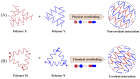
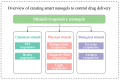
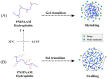
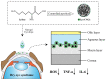
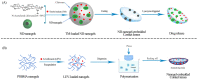
Nanotechnology has accelerated the development of the pharmaceutical and medical technology fields, and nanogels for ocular applications have proven to be a promising therapeutic strategy. Traditional ocular preparations are restricted by the anatomical and physiological barriers of the eye, resulting in a short retention time and low drug bioavailability, which is a significant challenge for physicians, patients, and pharmacists. Nanogels, however, have the ability to encapsulate drugs within three-dimensional crosslinked polymeric networks and, through specific structural designs and distinct methods of preparation, achieve the controlled and sustained delivery of loaded drugs, increasing patient compliance and therapeutic efficiency. In addition, nanogels have higher drug-loading capacity and biocompatibility than other nanocarriers. In this review, the main focus is on the applications of nanogels for ocular diseases, whose preparations and stimuli-responsive behaviors are briefly described. The current comprehension of topical drug delivery will be improved by focusing on the advances of nanogels in typical ocular diseases, including glaucoma, cataracts, dry eye syndrome, and bacterial keratitis, as well as related drug-loaded contact lenses and natural active substances.
Keywords: contact lenses; drug delivery systems; nanogels; natural polymers; ocular diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Developments in Emerging Topical Drug Delivery Systems for Ocular Disorders.Curr Drug Res Rev. 2024;16(3):251-267. doi: 10.2174/0125899775266634231213044704. Curr Drug Res Rev. 2024. PMID: 38158868 Review.
-
Native/modified dextran-based nanogel in delivering drug and management of ocular complications: a review.Z Naturforsch C J Biosci. 2025 Apr 29. doi: 10.1515/znc-2025-0014. Online ahead of print. Z Naturforsch C J Biosci. 2025. PMID: 40294585 Review.
-
Chemical, physical, and biological stimuli-responsive nanogels for biomedical applications (mechanisms, concepts, and advancements): A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2023 Jan 31;226:535-553. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.12.076. Epub 2022 Dec 12. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023. PMID: 36521697 Review.
-
Nanotechnology for Topical Drug Delivery to the Anterior Segment of the Eye.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 16;22(22):12368. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212368. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830247 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hydrogel-based ocular drug delivery systems for hydrophobic drugs.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2020 Nov 1;154:105503. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2020.105503. Epub 2020 Aug 1. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2020. PMID: 32745587 Review.
Cited by
-
Developments in Emerging Topical Drug Delivery Systems for Ocular Disorders.Curr Drug Res Rev. 2024;16(3):251-267. doi: 10.2174/0125899775266634231213044704. Curr Drug Res Rev. 2024. PMID: 38158868 Review.
-
Current perspectives in tackling glaucoma blindness.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2025 Mar 1;73(Suppl 2):S189-S196. doi: 10.4103/IJO.IJO_3280_23. Epub 2025 Feb 21. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 39982079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transforming Medicine with Nanobiotechnology: Nanocarriers and Their Biomedical Applications.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Aug 23;16(9):1114. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16091114. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39339152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advancements in nanomaterial-laden contact lenses for diagnosis and treatment of glaucoma, review and update.J Nanobiotechnology. 2023 Nov 2;21(1):402. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-02166-w. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023. PMID: 37919748 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ocular drug delivery systems based on nanotechnology: a comprehensive review for the treatment of eye diseases.Discov Nano. 2025 May 3;20(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s11671-025-04234-6. Discov Nano. 2025. PMID: 40317427 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bourne R., Steinmetz J.D., Flaxman S., Briant P.S., Taylor H.R., Resnikoff S., Casson R.J., Abdoli A., Abu-Gharbieh E., Afshin A., et al. Vision Loss Expert Group of the Global Burden of Disease Study Trends in Prevalence of Blindness and Distance and near Vision Impairment over 30 Years: An Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet Glob. Health. 2021;9:e130–e143. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhu M., Wang J., Li N. A Novel Thermo-Sensitive Hydrogel-Based on Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide)/Hyaluronic Acid of Ketoconazole for Ophthalmic Delivery. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018;46:1282–1287. - PubMed
-
- Sánchez-López E., Espina M., Doktorovova S., Souto E.B., García M.L. Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN, NLC): Overcoming the Anatomical and Physiological Barriers of the Eye—Part I—Barriers and Determining Factors in Ocular Delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. Off. J. Arbeitsgem. Pharm. Verfahr. EV. 2017;110:70–75. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

