Exploration of Reactive Black 5 Dye Desorption from Composite Hydrogel Beads-Adsorbent Reusability, Kinetic and Equilibrium Isotherms
- PMID: 37102910
- PMCID: PMC10137732
- DOI: 10.3390/gels9040299
Exploration of Reactive Black 5 Dye Desorption from Composite Hydrogel Beads-Adsorbent Reusability, Kinetic and Equilibrium Isotherms
Abstract
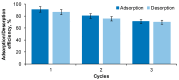
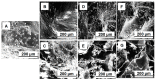
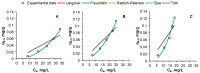
A low-cost adsorbent was prepared by using cherry stones powder and chitosan and used to retain Reactive Black 5 dye from aqueous solution. Then, the spent material was submitted to a regeneration process. Five different eluents (water, sodium hydroxide, hydrochloric acid, sodium chloride and ethanol) were tested. Among them, sodium hydroxide was selected for an advanced investigation. Values of three working conditions, namely the eluent volume, its concentration and the desorption temperature, were optimized by Response Surface Methodology-Box-Behnken Design. In the established settings (NaOH volume: 30 mL, NaOH concentration: 1.5 M, working temperature: 40 °C), three successive cycles of adsorption/desorption were conducted. The analysis performed by Scanning Electron Microscopy and by Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy revealed the evolution of the adsorbent throughout the dye elution from the material. Pseudo-second-order kinetic model and Freundlich equilibrium isotherm were able to accurately describe the desorption process. Based on the acquired results, our outcomes sustain the suitability of the synthesized material as dye adsorbent and the possibility of efficaciously recycling and reusing it.
Keywords: Box–Behnken Design; Reactive Black 5; cherry stones; chitosan; desorption; equilibrium isotherms; hydrogel beads; kinetics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Performance of Dye Removal from Single and Binary Component Systems by Adsorption on Composite Hydrogel Beads Derived from Fruits Wastes Entrapped in Natural Polymeric Matrix.Gels. 2022 Dec 3;8(12):795. doi: 10.3390/gels8120795. Gels. 2022. PMID: 36547319 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient removal of crystal violet dye from aqueous solutions using sodium hydroxide-modified avocado shells: kinetics and isotherms modeling.Water Sci Technol. 2022 Jan;85(1):433-448. doi: 10.2166/wst.2021.451. Water Sci Technol. 2022. PMID: 35050894
-
Batch Adsorption of Orange II Dye on a New Green Hydrogel-Study on Working Parameters and Process Enhancement.Gels. 2025 Jan 20;11(1):79. doi: 10.3390/gels11010079. Gels. 2025. PMID: 39852050 Free PMC article.
-
Adsorptive removal of anionic dye (Reactive Black 5) from aqueous solution using chemically modified banana peel powder: kinetic, isotherm, thermodynamic, and reusability studies.Int J Phytoremediation. 2020;22(3):267-278. doi: 10.1080/15226514.2019.1658709. Epub 2019 Aug 29. Int J Phytoremediation. 2020. PMID: 31464513
-
Hydrogels Based on Chitosan and Nanoparticles and Their Suitability for Dyes Adsorption from Aqueous Media: Assessment of the Last-Decade Progresses.Gels. 2024 Mar 21;10(3):211. doi: 10.3390/gels10030211. Gels. 2024. PMID: 38534629 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Strong Amphoteric Adsorption of Reactive Red-141 onto Modified Orange Peel Derivatives: Optimization, Characterization, and Mechanism.Polymers (Basel). 2025 Jul 4;17(13):1875. doi: 10.3390/polym17131875. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40647884 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sauvé S., Bernard S., Sloan P. Environmental sciences, sustainable development and circular economy: Alternative concepts for trans-disciplinary research. Environ. Dev. 2016;17:48–56. doi: 10.1016/j.envdev.2015.09.002. - DOI
-
- Shi Y., Chang Q., Zhang T., Song G., Sun Y., Ding G. A review on selective dye adsorption by different mechanisms. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022;10:108639. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2022.108639. - DOI
-
- Osagie C., Othmani A., Ghosh S., Malloum A., Kashitarash Esfahani Z., Ahmadi S. Dyes adsorption from aqueous media through the nanotechnology: A review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021;14:2195–2218. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.07.085. - DOI
-
- Duarte E.D.V., Oliveira M.G., Spaolonzi M.P., Costa H.P.S., Silva T.L.d., Silva M.G.C.d., Vieira M.G.A. Adsorption of pharmaceutical products from aqueous solutions on functionalized carbon nanotubes by conventional and green methods: A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2022;372:133743. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.133743. - DOI
-
- Zhu X., He M., Sun Y., Xu Z., Wan Z., Hou D., Alessi D.S., Tsang D.C.W. Insights into the adsorption of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) on biochar and activated carbon with the aid of machine learning. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022;423:127060. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127060. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

