The Use of Hydrogel-Based Materials for Radioprotection
- PMID: 37102914
- PMCID: PMC10137482
- DOI: 10.3390/gels9040301
The Use of Hydrogel-Based Materials for Radioprotection
Abstract
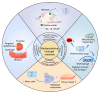
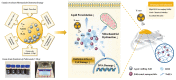
Major causes of the radiation-induced disease include nuclear accidents, war-related nuclear explosions, and clinical radiotherapy. While certain radioprotective drug or bioactive compounds have been utilized to protect against radiation-induced damage in preclinical and clinical settings, these strategies are hampered by poor efficacy and limited utilization. Hydrogel-based materials are effective carriers capable of enhancing the bioavailability of compounds loaded therein. As they exhibit tunable performance and excellent biocompatibility, hydrogels represent promising tools for the design of novel radioprotective therapeutic strategies. This review provides an overview of common approaches to radioprotective hydrogel preparation, followed by a discussion of the pathogenesis of radiation-induced disease and the current states of research focused on using hydrogels to protect against these diseases. These findings ultimately provide a foundation for discussions of the challenges and future prospects associated with the use of radioprotective hydrogels.
Keywords: hydrogels; radiation injury; radioprotection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Indian Indigenous Fruits as Radioprotective Agents: Past, Present and Future.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2022;22(1):53-63. doi: 10.2174/1871520621666210706124315. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 34229590 Review.
-
Radioprotective effects of induced astronaut torpor and advanced propulsion systems during deep space travel.Life Sci Space Res (Amst). 2020 Aug;26:105-113. doi: 10.1016/j.lssr.2020.05.005. Epub 2020 Jun 10. Life Sci Space Res (Amst). 2020. PMID: 32718676
-
Design and evaluation of pH-responsive hydrogel for oral delivery of amifostine and study on its radioprotective effects.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020 Nov;195:111200. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2020.111200. Epub 2020 Jun 18. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020. PMID: 32623053
-
Intelligent Hydrogel-Assisted Hepatocellular Carcinoma Therapy.Research (Wash D C). 2024 Oct 14;7:0477. doi: 10.34133/research.0477. eCollection 2024. Research (Wash D C). 2024. PMID: 39691767 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancements in delivery systems for dietary polyphenols in enhancing radioprotection effects: challenges and opportunities.NPJ Sci Food. 2025 Apr 14;9(1):51. doi: 10.1038/s41538-025-00419-6. NPJ Sci Food. 2025. PMID: 40229284 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Toon O.B., Bardeen C.G., Robock A., Xia L., Kristensen H., McKinzie M., Peterson R.J., Harrison C.S., Lovenduski N.S., Turco R.P. Rapidly expanding nuclear arsenals in Pakistan and India portend regional and global catastrophe. Sci. Adv. 2019;5:y5478. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aay5478. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ohba T., Liutsko L., Schneider T., Barquinero J.F., Crouaïl P., Fattibene P., Kesminiene A., Laurier D., Sarukhan A., Skuterud L., et al. The SHAMISEN Project: Challenging historical recommendations for preparedness, response and surveillance of health and well-being in case of nuclear accidents: Lessons learnt from Chernobyl and Fukushima. Environ. Int. 2021;146:106200. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.106200. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

