Rosuvastatin Attenuates Progression of Atherosclerosis and Reduces Serum IL6 and CCL2 Levels in Apolipoprotein-E-deficient Mice
- PMID: 37103114
- PMCID: PMC10188013
- DOI: 10.21873/invivo.13173
Rosuvastatin Attenuates Progression of Atherosclerosis and Reduces Serum IL6 and CCL2 Levels in Apolipoprotein-E-deficient Mice
Abstract
Background/aim: Apolipoprotein E-deficient (Apoe-/-) mice develop atherosclerotic lesions that closely resemble metabolic syndrome in humans. We sought to investigate how rosuvastatin mitigates the atherosclerotic profile of Apoe-/- mice over time and its effects on certain inflammatory chemokines.
Materials and methods: Eighteen Apoe-/- mice were allocated into three groups of six mice each receiving: standard chow diet (SCD; control group); high-fat diet (HFD); and HFD and rosuvastatin at 5 mg/kg/d orally via gavage for 20 weeks. Analysis of aortic plaques and lipid deposition was conducted by means of en face Sudan IV staining and Oil Red O staining. Serum cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein, high-density lipoprotein, plasma glucose and triglyceride levels were determined at baseline and after 20 weeks of treatment. Serum interleukin 6 (IL6), C-C motif chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNFα) levels were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay at the time of euthanasia.
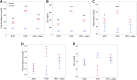
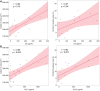
Results: The lipidemic profile of Apoe-/- mice on HFD deteriorated over time. Apoe-/- mice on HFD developed atherosclerotic lesions over time. Sudan IV and Oil Red O-stained sections of the aorta revealed increased plaque formation and plaque lipid deposition in HFD-fed mice compared with SCD-fed mice and reduced plaque development in HFD-fed mice treated with rosuvastatin compared with mice not receiving statin treatment. Serum analysis revealed reduced metabolic parameters in HFD-fed mice on rosuvastatin compared with non-statin, HFD-fed mice. At the time of euthanasia, HFD-fed mice treated with rosuvastatin had significantly lower IL6 as well as CCL2 levels when compared with HFD-fed mice not receiving rosuvastatin. TNFα levels were comparable among all groups of mice, irrespective of treatment. IL6 and CCL2 positively correlated with the extent of atherosclerotic lesions and lipid deposition in atherosclerotic plaques.
Conclusion: Serum IL6 and CCL2 levels might potentially be used as clinical markers of progression of atherosclerosis during statin treatment for hypercholesterolemia.
Keywords: APOE; CCL2; IL6; Rosuvastatin; atherosclerosis; mouse.
Copyright © 2023, International Institute of Anticancer Research (Dr. George J. Delinasios), All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Impact of rosuvastatin on atherosclerosis lesions in apolipoprotein E knockout mice].Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2011 Aug;39(8):743-8. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 22169423 Chinese.
-
Small leucine-rich proteoglycans in atherosclerotic lesions: novel targets of chronic statin treatment?J Cell Mol Med. 2011 Feb;15(2):232-43. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00986.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 20015203 Free PMC article.
-
Lipingshu capsule improves atherosclerosis associated with lipid regulation and inflammation inhibition in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice.Lipids Health Dis. 2018 Jul 31;17(1):182. doi: 10.1186/s12944-018-0823-4. Lipids Health Dis. 2018. PMID: 30064511 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of hydroxychloroquine on rheumatoid arthritis-associated atherosclerosis.Animal Model Exp Med. 2019 Apr 19;2(2):98-106. doi: 10.1002/ame2.12065. eCollection 2019 Jun. Animal Model Exp Med. 2019. PMID: 31392302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel mechanisms and therapeutic targets in atherosclerosis: inflammation and beyond.Eur Heart J. 2023 Aug 1;44(29):2672-2681. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehad304. Eur Heart J. 2023. PMID: 37210082 Review.
Cited by
-
Rosuvastatin-Based Lipid-Lowering Therapy for the Control of LDL Cholesterol in Patients at High Vascular Risk.J Clin Med. 2024 Mar 25;13(7):1894. doi: 10.3390/jcm13071894. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38610659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of DPP-4 Inhibitors on Interleukin Levels in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2025 Mar 17;110(4):1195-1204. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgae783. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2025. PMID: 39512193 Free PMC article.
-
Oral Nanoformulations in Cardiovascular Medicine: Advances in Atherosclerosis Treatment.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jul 10;17(7):919. doi: 10.3390/ph17070919. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39065770 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The beneficial effects of Rosuvastatin in inhibiting inflammation in sepsis.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Jun 14;16(12):10424-10434. doi: 10.18632/aging.205937. Epub 2024 Jun 14. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38885061 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
