Guided Bone Regeneration in a Periodontally Compromised Individual with Autogenous Tooth Bone Graft: A Radiomics Analysis
- PMID: 37103310
- PMCID: PMC10142001
- DOI: 10.3390/jfb14040220
Guided Bone Regeneration in a Periodontally Compromised Individual with Autogenous Tooth Bone Graft: A Radiomics Analysis
Abstract
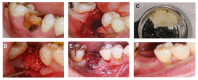
Background: Autogenous tooth bone graft material (AutoBT) has been advocated as a bone substitute when conducting alveolar ridge preservation. This study is aimed at using a radiomics approach in order to evaluate and testify whether AutoBT can stimulate bone growth during socket preservation in severe periodontal cases.
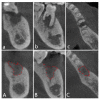
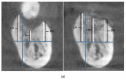
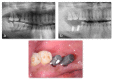
Materials and methods: For this study, 25 cases with severe periodontal diseases were selected. The patients' AutoBTs were inserted into the extraction sockets and covered with Bio-Gide® collagen membranes. 3D CBCT scans and 2D X-rays were taken of the patients before surgery and after 6 months post-surgery. For the retrospective radiomics analysis, the maxillary and mandibular images were compared in different groups. Maxillary bone height was analyzed at the buccal, middle, and palatal crest sites, while the mandibular bone height was compared at the buccal, center, and lingual crest sites.
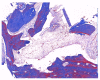
Results: In the maxilla, the alveolar height was increased by -2.15 ± 2.90 mm at the buccal crest; -2.45 ± 2.36 mm at the center of the socket, and -1.62 ± 3.19 mm at the palatal crest, while the height of the buccal crest was increased by 0.19 ± 3.52 mm, and the height at the center of the socket was increased by -0.70 ± 2.71 mm in the mandible. The three-dimensional radiomics analysis demonstrated significant bone growth in the local alveolar height and high density.
Conclusion: Based on clinical radiomics analysis, AutoBT could be used as an alternative bone material in socket preservation after tooth extraction in patients with severe periodontitis.
Keywords: CBCT scans; artificial bone grafting; autogenous tooth bone graft material (AutoBT); severe periodontitis; socket preservation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Radiographic evaluation of ridge preservation after molar tooth extraction: a controlled clinical trial].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2015 Feb 18;47(1):19-26. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2015. PMID: 25686323 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
[Evaluation with different measuring methods for the alveolar bone change of ridge preservation in molar sites].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2016 Feb 18;48(1):126-32. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2016. PMID: 26885922 Chinese.
-
Autogenous demineralized dentin matrix from extracted tooth for the augmentation of alveolar bone defect: a prospective randomized clinical trial in comparison with anorganic bovine bone.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2017 Jul;28(7):809-815. doi: 10.1111/clr.12885. Epub 2016 Jun 8. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2017. PMID: 27279547 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of alveolar ridge preservation interventions following tooth extraction: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Clin Periodontol. 2019 Jun;46 Suppl 21:195-223. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.13057. J Clin Periodontol. 2019. PMID: 30623987
-
Autogenous Tooth Bone Grafts for Repair and Regeneration of Maxillofacial Defects: A Narrative Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Mar 20;19(6):3690. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19063690. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35329377 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regenerative Surgical Management of an Endodontic Periodontic Lesion of the Mandibular Molar Combined With External Inflammation Root Resorption.Case Rep Dent. 2024 Aug 29;2024:1048933. doi: 10.1155/2024/1048933. eCollection 2024. Case Rep Dent. 2024. PMID: 39239239 Free PMC article.
-
Photobiomodulation Therapy Improves Repair of Bone Defects Filled by Inorganic Bone Matrix and Fibrin Heterologous Biopolymer.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 Jan 13;11(1):78. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11010078. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38247955 Free PMC article.
-
Regeneration of Rabbit Calvarial Defects with Combination of Stem Cells and Enamel Matrix Derivative: A Microcomputed Tomography and Histological Evaluation Comparing Two- and Three-Dimensional Cell Constructs.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Mar 8;60(3):451. doi: 10.3390/medicina60030451. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 38541178 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wu H., Qiu W., Zhu X., Li X., Xie Z., Carreras I., Dedeoglu A., Van Dyke T., Han Y.W., Karimbux N., et al. The Periodontal Pathogen Fusobacterium nucleatum Exacerbates Alzheimer’s Pathogenesis via Specific Pathways. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022;14:912709. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.912709. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

