Peptide-Based Hydrogels: Template Materials for Tissue Engineering
- PMID: 37103323
- PMCID: PMC10145623
- DOI: 10.3390/jfb14040233
Peptide-Based Hydrogels: Template Materials for Tissue Engineering
Abstract
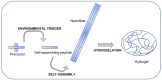
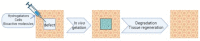
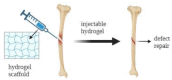
Tissue and organ regeneration are challenging issues, yet they represent the frontier of current research in the biomedical field. Currently, a major problem is the lack of ideal scaffold materials' definition. As well known, peptide hydrogels have attracted increasing attention in recent years thanks to significant properties such as biocompatibility, biodegradability, good mechanical stability, and tissue-like elasticity. Such properties make them excellent candidates for 3D scaffold materials. In this review, the first aim is to describe the main features of a peptide hydrogel in order to be considered as a 3D scaffold, focusing in particular on mechanical properties, as well as on biodegradability and bioactivity. Then, some recent applications of peptide hydrogels in tissue engineering, including soft and hard tissues, will be discussed to analyze the most relevant research trends in this field.
Keywords: 3D scaffolds; peptide hydrogels; self-assembly; tissue engineering.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Synthetic peptide hydrogels as 3D scaffolds for tissue engineering.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2020;160:78-104. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2020.10.005. Epub 2020 Oct 19. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2020. PMID: 33091503
-
Peptide-Based Hydrogels: New Materials for Biosensing and Biomedical Applications.Materials (Basel). 2022 Aug 25;15(17):5871. doi: 10.3390/ma15175871. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36079250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polyethylene glycol diacrylate scaffold filled with cell-laden methacrylamide gelatin/alginate hydrogels used for cartilage repair.J Biomater Appl. 2022 Jan;36(6):1019-1032. doi: 10.1177/08853282211044853. Epub 2021 Oct 4. J Biomater Appl. 2022. PMID: 34605703
-
Bi-functional peptide-based 3D hydrogel-scaffolds.Soft Matter. 2020 Aug 5;16(30):7006-7017. doi: 10.1039/d0sm00825g. Soft Matter. 2020. PMID: 32638818
-
Advances in bioactive glass-containing injectable hydrogel biomaterials for tissue regeneration.Acta Biomater. 2021 Dec;136:1-36. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2021.09.034. Epub 2021 Sep 23. Acta Biomater. 2021. PMID: 34562661 Review.
Cited by
-
Biosynthesis of Peptide Hydrogel-Titania Nanoparticle Composites with Antibacterial Properties.Gels. 2023 Nov 30;9(12):940. doi: 10.3390/gels9120940. Gels. 2023. PMID: 38131926 Free PMC article.
-
Injectable self-assembled GDF5-containing dipeptide hydrogels for enhanced tendon repair.Mater Today Bio. 2024 Apr 3;26:101046. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.101046. eCollection 2024 Jun. Mater Today Bio. 2024. PMID: 38600922 Free PMC article.
-
Peptide Hydrogel for Sustained Release of Recombinant Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 In Vitro.J Funct Biomater. 2024 Dec 6;15(12):369. doi: 10.3390/jfb15120369. J Funct Biomater. 2024. PMID: 39728169 Free PMC article.
-
A Review on the Rheological Properties of Single Amino Acids and Short Dipeptide Gels.Gels. 2024 Aug 1;10(8):507. doi: 10.3390/gels10080507. Gels. 2024. PMID: 39195036 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functionalized Surface Coatings for Rigid Contact Lenses.J Funct Biomater. 2024 Jun 5;15(6):154. doi: 10.3390/jfb15060154. J Funct Biomater. 2024. PMID: 38921528 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chandra P.K., Soker S., Atala A. Principles of Tissue Engineering. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2020.
-
- Hoffman T., Antovski P., Tebon P., Xu C., Ashammakhi N., Ahadian S., Morsut L., Khademhosseini A. Synthetic Biology and Tissue Engineering: Toward Fabrication of Complex and Smart Cellular Constructs. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020;30:1909882. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201909882. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

