Glycosaminoglycans from the Starfish Lethasterias fusca: Structures and Influence on Hematopoiesis
- PMID: 37103344
- PMCID: PMC10146216
- DOI: 10.3390/md21040205
Glycosaminoglycans from the Starfish Lethasterias fusca: Structures and Influence on Hematopoiesis
Abstract
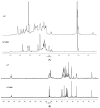
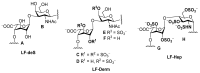
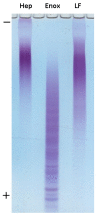
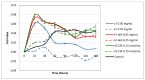
Crude anionic polysaccharides extracted from the Pacific starfish Lethasterias fusca were purified by anion-exchange chromatography. The main fraction LF, having MW 14.5 kDa and dispersity 1.28 (data of gel-permeation chromatography), was solvolytically desulfated and giving rise to preparation LF-deS with a structure of dermatan core [→3)-β-d-GalNAc-(1→4)-α-l-IdoA-(1→]n, which was identified according to NMR spectroscopy data. Analysis of the NMR spectra of the parent fraction LF led to identification of the main component as dermatan sulfate LF-Derm →3)-β-d-GalNAc4R-(1→4)-α-l-IdoA2R3S-(1→ (where R was SO3 or H), bearing sulfate groups at O-3 or both at O-2 and O-3 of α-l-iduronic acid, as well as at O-4 of some N-acetyl-d-galactosamine residues. The minor signals in NMR spectra of LF were assigned as resonances of heparinoid LF-Hep composed of the fragments →4)-α-d-GlcNS3S6S-(1→4)-α-l-IdoA2S3S-(1→. The 3-O-sulfated and 2,3-di-O-sulfated iduronic acid residues are very unusual for natural glycosaminoglycans, and further studies are needed to elucidate their possible specific influence on the biological activity of the corresponding polysaccharides. To confirm the presence of these units in LF-Derm and LF-Hep, a series of variously sulfated model 3-aminopropyl iduronosides were synthesized and their NMR spectra were compared with those of the polysaccharides. Preparations LF and LF-deS were studied as stimulators of hematopoiesis in vitro. Surprisingly, it was found that both preparations were active in these tests, and hence, the high level of sulfation is not necessary for hematopoiesis stimulation in this particular case.
Keywords: Lethasterias fusca; dermatan sulfate; hematopoiesis; heparinoid; starfish; synthetic sulfated iduronosides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Oversulfated dermatan sulfate and heparinoid in the starfish Lysastrosoma anthosticta: Structures and anticoagulant activity.Carbohydr Polym. 2021 Jun 1;261:117867. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.117867. Epub 2021 Feb 25. Carbohydr Polym. 2021. PMID: 33766355
-
Structure and anticoagulant properties of sulfated glycosaminoglycans from primitive Chordates.An Acad Bras Cienc. 2002 Mar;74(1):105-12. doi: 10.1590/s0001-37652002000100007. An Acad Bras Cienc. 2002. PMID: 11960179 Review.
-
A unique dermatan sulfate-like glycosaminoglycan from ascidian. Its structure and the effect of its unusual sulfation pattern on anticoagulant activity.J Biol Chem. 1995 Dec 29;270(52):31027-36. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.52.31027. J Biol Chem. 1995. PMID: 8537360
-
Highly sulfated dermatan sulfates from Ascidians. Structure versus anticoagulant activity of these glycosaminoglycans.J Biol Chem. 1998 Oct 23;273(43):27848-57. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.43.27848. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9774395
-
Biological function of unique sulfated glycosaminoglycans in primitive chordates.Glycoconj J. 2017 Jun;34(3):277-283. doi: 10.1007/s10719-016-9728-5. Epub 2016 Sep 10. Glycoconj J. 2017. PMID: 27614617 Review.
Cited by
-
Antioxidant and antiproliferative effect of a glycosaminoglycan extract from Rapana venosa marine snail.PLoS One. 2024 Feb 15;19(2):e0297803. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0297803. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38359063 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kochetkov N.K., Smirnova G.P. Glycolipids of marine invertebrates. Adv. Carbohydr. Chem. Biochem. 1986;44:387–438. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2318(08)60082-7. - DOI
-
- Smirnova G.P. Gangliosides of starfishes: Variety and possible species specificity of structures. Russ. J. Mar. Biol. 1987;1:3–7.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

