Chitosan Nanoparticles-Based Cancer Drug Delivery: Application and Challenges
- PMID: 37103352
- PMCID: PMC10142570
- DOI: 10.3390/md21040211
Chitosan Nanoparticles-Based Cancer Drug Delivery: Application and Challenges
Abstract
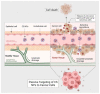
Chitin is the second most abundant biopolymer consisting of N-acetylglucosamine units and is primarily derived from the shells of marine crustaceans and the cell walls of organisms (such as bacteria, fungi, and algae). Being a biopolymer, its materialistic properties, such as biodegradability, and biocompatibility, make it a suitable choice for biomedical applications. Similarly, its deacetylated derivative, chitosan, exhibits similar biocompatibility and biodegradability properties, making it a suitable support material for biomedical applications. Furthermore, it has intrinsic material properties such as antioxidant, antibacterial, and antitumor. Population studies have projected nearly 12 million cancer patients across the globe, where most will be suffering from solid tumors. One of the shortcomings of potent anticancer drugs is finding a suitable cellular delivery material or system. Therefore, identifying new drug carriers to achieve effective anticancer therapy is becoming essential. This paper focuses on the strategies implemented using chitin and chitosan biopolymers in drug delivery for cancer treatment.
Keywords: anticancer agents; chitin; chitosan; nanocarriers; nanoparticles; polysaccharides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Wysokowski M., Machałowski T., Petrenko I., Schimpf C., Rafaja D., Galli R., Ziętek J., Pantović S., Voronkina A., Kovalchuk V., et al. 3D Chitin Scaffolds of Marine Demosponge Origin for Biomimetic Mollusk Hemolymph-Associated Biomineralization Ex-Vivo. Mar. Drugs. 2020;18:123. doi: 10.3390/md18020123. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mutsenko V.V., Gryshkov O., Lauterboeck L., Rogulska O., Tarusin D.N., Bazhenov V.V., Schütz K., Brüggemeier S., Gossla E., Akkineni A.R., et al. Novel Chitin Scaffolds Derived from Marine Sponge Ianthella Basta for Tissue Engineering Approaches Based on Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: Biocompatibility and Cryopreservation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017;104:1955–1965. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.03.161. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wysokowski M., Petrenko I., Stelling A., Stawski D., Jesionowski T., Ehrlich H. Poriferan Chitin as a Versatile Template for Extreme Biomimetics. Polymers. 2015;7:235–265. doi: 10.3390/polym7020235. - DOI
-
- Petrenko I., Bazhenov V.V., Galli R., Wysokowski M., Fromont J., Schupp P.J., Stelling A.L., Niederschlag E., Stöker H., Kutsova V.Z., et al. Chitin of Poriferan Origin and the Bioelectrometallurgy of Copper/Copper Oxide. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017;104:1626–1632. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.01.084. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

