Predicting Responses to Hypertonic Saline: Edelman's Evidence, Elementary Algebra, and Eponyms
- PMID: 37103958
- PMCID: PMC10371361
- DOI: 10.34067/KID.0000000000000105
Predicting Responses to Hypertonic Saline: Edelman's Evidence, Elementary Algebra, and Eponyms
Figures
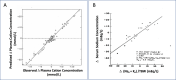
Comment on
-
Hypertonic Saline Infusion for Hyponatremia: Limitations of the Adrogué-Madias and Other Formulas.Kidney360. 2023 Apr 1;4(4):e555-e561. doi: 10.34067/KID.0000000000000075. Epub 2023 Feb 10. Kidney360. 2023. PMID: 36758190 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

