Comparison of Automated and Traditional Western Blotting Methods
- PMID: 37104025
- PMCID: PMC10142486
- DOI: 10.3390/mps6020043
Comparison of Automated and Traditional Western Blotting Methods
Abstract
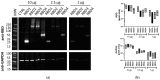
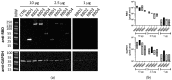
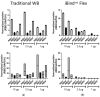
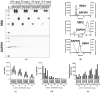
Traditional Western blotting is one of the most used analytical techniques in biological research. However, it can be time-consuming and suffer from a lack of reproducibility. Consequently, devices with different degrees of automation have been developed. These include semi-automated techniques and fully automated devices that replicate all stages downstream of the sample preparation, including sample size separation, immunoblotting, imaging, and analysis. We directly compared traditional Western blotting with two different automated systems, iBind™ Flex, which is a semi-automated system designed to perform the immunoblotting, and JESS Simple Western™, a fully automated and capillary-based system performing all steps downstream of sample preparation and loading, including imaging and image analysis. We found that a fully automated system can save time and importantly offer valuable sensitivity. This is particularly beneficial for limited sample amounts. The downside of automation is the cost of devices and reagents. Nevertheless, automation can be a good option to increase output and facilitate sensitive protein analyses.
Keywords: JESS Simple Western™; SARS-CoV-2; Western blotting; automation; iBind™ Flex; protein analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Using the Peggy Simple Western system for fine needle aspirate analysis.Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1219:139-55. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-1661-0_11. Methods Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25308267
-
Qualitative and quantitative evaluation of Simon™, a new CE-based automated Western blot system as applied to vaccine development.Electrophoresis. 2012 Sep;33(17):2790-7. doi: 10.1002/elps.201200095. Electrophoresis. 2012. PMID: 22965727
-
Simple Western: Bringing the Western Blot into the Twenty-First Century.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2261:481-488. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1186-9_30. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33421009
-
Protein purification and analysis: next generation Western blotting techniques.Expert Rev Proteomics. 2017 Nov;14(11):1037-1053. doi: 10.1080/14789450.2017.1388167. Epub 2017 Oct 13. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2017. PMID: 28974114 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Automation of mass spectrometric detection of analytes and related workflows: A review.Talanta. 2020 Feb 1;208:120304. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2019.120304. Epub 2019 Aug 29. Talanta. 2020. PMID: 31816721 Review.
Cited by
-
Glucose Fluctuation Inhibits Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in Hippocampal Tissues and Exacerbates Cognitive Impairment in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats.J Diabetes Res. 2024 Jan 19;2024:5584761. doi: 10.1155/2024/5584761. eCollection 2024. J Diabetes Res. 2024. PMID: 38282656 Free PMC article.
-
Quantification of AMPA receptor subunits and RNA editing-related proteins in the J20 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease by capillary western blotting.Front Mol Neurosci. 2024 Jan 17;16:1338065. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2023.1338065. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38299128 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic Analyses Reveal the Role of Alpha-2-Macroglobulin in Canine Osteosarcoma Cell Migration.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 3;25(7):3989. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073989. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612805 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of recombinant human lactoferrin expressed in Komagataella phaffii.Analyst. 2024 Jun 24;149(13):3636-3650. doi: 10.1039/d4an00333k. Analyst. 2024. PMID: 38814097 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotype Differences Between ATP13A2 Heterozygous and Knockout Mice Across Aging.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 22;26(15):7030. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157030. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806164 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

