Home working and social and mental wellbeing at different stages of the COVID-19 pandemic in the UK: Evidence from 7 longitudinal population surveys
- PMID: 37104282
- PMCID: PMC10138202
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1004214
Home working and social and mental wellbeing at different stages of the COVID-19 pandemic in the UK: Evidence from 7 longitudinal population surveys
Abstract
Background: Home working has increased since the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic's onset with concerns that it may have adverse health implications. We assessed the association between home working and social and mental wellbeing among the employed population aged 16 to 66 through harmonised analyses of 7 UK longitudinal studies.
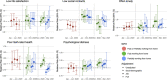
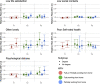
Methods and findings: We estimated associations between home working and measures of psychological distress, low life satisfaction, poor self-rated health, low social contact, and loneliness across 3 different stages of the pandemic (T1 = April to June 2020 -first lockdown, T2 = July to October 2020 -eased restrictions, T3 = November 2020 to March 2021 -second lockdown) using modified Poisson regression and meta-analyses to pool results across studies. We successively adjusted the model for sociodemographic characteristics (e.g., age, sex), job characteristics (e.g., sector of activity, pre-pandemic home working propensities), and pre-pandemic health. Among respectively 10,367, 11,585, and 12,179 participants at T1, T2, and T3, we found higher rates of home working at T1 and T3 compared with T2, reflecting lockdown periods. Home working was not associated with psychological distress at T1 (RR = 0.92, 95% CI = 0.79 to 1.08) or T2 (RR = 0.99, 95% CI = 0.88 to 1.11), but a detrimental association was found with psychological distress at T3 (RR = 1.17, 95% CI = 1.05 to 1.30). Study limitations include the fact that pre-pandemic home working propensities were derived from external sources, no information was collected on home working dosage and possible reverse association between change in wellbeing and home working likelihood.
Conclusions: No clear evidence of an association between home working and mental wellbeing was found, apart from greater risk of psychological distress during the second lockdown, but differences across subgroups (e.g., by sex or level of education) may exist. Longer term shifts to home working might not have adverse impacts on population wellbeing in the absence of pandemic restrictions but further monitoring of health inequalities is required.
Copyright: © 2023 Wels et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
I have read the journal’s policy and the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests: SVK is a member of the Scientific Advisory Group on Emergencies, the other authors report no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Bolisani E, Scarso E, Ipsen C, Kirchner K, Hansen JP. Working from home during COVID-19 pandemic: Lessons learned and issues. Management and Marketing. 2020;15:458–476. doi: 10.2478/mmcks-2020-0027 - DOI
-
- Bloom N, Han R, Liang J. How Hybrid Working From Home Works Out. NBER Working Paper. 2022;30292:1–52.
-
- Brynjolfsson E, Horton JJ, Ozimek A, Rock D, Sharma G, Tuye H-Y, et al.. COVID-19 and Remote Work: An Early Look at US Data. NBER Working Paper. 2020;27344:1–26.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- MR/S037527/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 104036/Z/14/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MR/W021277/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/N024397/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- CS/16/4/32482/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_20030/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- SCAF/15/02/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_00022/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 216767/Z/19/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_20059/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- WT101597MA/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_00019/3/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous